Projectile Motion: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (129 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Edited by YorickAndeweg June 2019''' | |||
'''Edited by Richard Udall July 2019''' | |||
'''Edited by Sarah Kilgore November 2022''' | |||
'''Edited by Audrey Cho April 2024''' | |||
Motion in which an object is affected only by the constant force of gravity is referred to as projectile motion (and the object as a projectile). This scenario is necessarily a simplification, since one larger scales gravity is not constant as one moves away from the attracting object, and there is also usually air resistance acting upon the object. However, it is a useful approximation, and an instructive use of kinematics. | |||
==The Main Idea== | ==The Main Idea== | ||
Projectile motion is a branch of classical mechanics which analyzes the motion of objects (projectiles) under the influence of the constant acceleration of gravity near the surface of the earth.<ref> https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/Lesson-2/What-is-a-Projectile </ref> Often, the projectiles are propelled prior to being analyzed under the influence of gravity, giving them initial velocities that affect their trajectories. Two classic examples of projectile motion are the firing of a cannon and throwing a ball off a tower. An object is a projectile if it is subject only to the constant force of gravity. For real projectiles, other forces such as air resistance are usually present, but these make the mathematical model significantly more complicated, and fair estimations may be gotten when disregarding them for many cases (note, however, that the relative importance of these forces increases for a feather vs for a ball). Regardless of the direction of motion of the projectile, the free-body diagram of a projectile is always the same, and constant throughout its trajectory: a particle on which only gravity acts in a downward direction. | |||
===Properties=== | |||
[[File:parabolic-motion.png|right]] | |||
1. Motion is considered parabolic. <br /> | |||
2. Horizontal component of acceleration is considered to be zero. <br /> | |||
3. Vertical component of acceleration is constant because of gravity. <br /> | |||
4. Horizontal and Vertical motion components are independent but share the same time. <br /> | |||
===A Mathematical Model=== | ===A Mathematical Model=== | ||
Traditionally, the [[Frame of Reference]] chosen for projectile motion problems places the origin on the ground below the point of launch and defines t=0 to be the time of launch.The +y direction is usually defined as vertically upwards, so the gravitational force acts in the -y direction. Because there will be no forces horizontal to the ground, it is possible to define our coordinate system with the +x direction as the direction of the horizontal component of the projectile's velocity, and in doing so ignore the third dimension altogether. The y component of the velocity is constantly changing over time due to the gravitational force. Gravity near the surface of the earth causes a constant downward acceleration of 9.8m/s^2. This causes a parabolic trajectory. The constant velocity in the x direction and the constant acceleration in the y direction lend themselves to the Kinematic Equations. [[Kinematics]] are used to analytically solve problems related to projectile motion. | |||
The following equations derived from kinematics describe the x and y components of a projectile's position as functions of time.<ref> http://webhome.phy.duke.edu/~rgb/Class/intro_physics_1/intro_physics_1.pdf </ref> | |||
<math>y(t) = - \frac{1}{2} g \cdot t^2 + v_{y, 0} \cdot t + y_i</math> | |||
<math>x(t) = v_{x, 0} \cdot t </math> | |||
It is evident from the above equations that the two components of a projectile's motion are independent; the particle's horizontal position has no effect on its vertical motion and vice versa. | |||
<math>v_{y, 0}</math> and <math>v_{y, 0}</math> may each be positive, negative, or 0, depending on how the projectile was launched, resulting in a variety of trajectory shapes. Below are some possible trajectories of projectiles: | |||
[[File:ProjectileMotionShapes.jpg]] | |||
Note that all of these shapes are parabolic. | |||
Sometimes, an initial speed and an initial angle (usually with respect to the horizontal) is given. In this case, <math>v_{y, 0} = v_0 \sin \theta_0</math> and <math>v_{x, 0} = v_0 \cos \theta_0</math>. | |||
Sometimes, rather than giving an initial velocity, a projectile motion problem will give the mass of the projectile as well as the magnitude, direction, and duration of the propelling force launching it. From this information, the relationship between [[Impulse and Momentum]] can be used to find the initial velocity of the projectile. In these situations, the propelling force is usually considered the only force acting on the object during the pre-trajectory impulse, because even if other forces are present, they are usually negligible compared to the propelling force. | |||
At the highest point in a projectile's trajectory, the projectile's velocity is entirely horizontal; the vertical component is 0. This is because at that point in time, the vertical velocity has stopped being positive and is no longer carrying the projectile higher, but has not yet become negative and has therefore not begun lowering the projectile once more. | |||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
One method used to visualize or predict a projectiles trajectory is to apply our mathematical model using computational programming. Computer models usually use [[Iterative Prediction]] rather than [[Kinematics]] to determine the path of the projectile. Here is an example of a program in vPython that simulates a projectile: | |||
[https://www.glowscript.org/#/user/YorickAndeweg/folder/PhysicsBookFolder/program/IterativePrediction1 Simulation of Projectile] | |||
Click "view this program" on the top left corner to view the source code. | |||
When working with algebraic solutions such as this one, one may also make use of analytic solution engines such as Mathematica or Maple. The same snippet of code describing projectile motion is used here and in [[Kinematics]]: | |||
<code>(*First Cell*) | |||
(*Setup for a generic projectile motion problem*) | |||
launchspeed = 10 | |||
launchangle = Pi/6 | |||
vinit = launchspeed*{Cos[launchangle], Sin[launchangle], 0} | |||
launchpos = {0, 0, 0} | |||
yterminus = 0 | |||
g = 9.8</code> | |||
Naturally, one can edit these values to set up a different problem. The setup and the equation solution itself is separated into two cells (Mathematica has a cell notebook based structure) for cleanliness' sake. | |||
<code>(*Second Cell*) | |||
(*Solving for the time of impact, then plugging that in to the original equations to find position in x and y *) | |||
T = Solve[-g*t^2/2 + vinit<nowiki>[[2]]</nowiki>*t + launchpos<nowiki>[[2]]</nowiki> == yterminus, t] | |||
finalpos = {(vinit<nowiki>[[1]]</nowiki>*t + launchpos<nowiki>[[1]]</nowiki>) /. T, (-g*t^2/2 + vinit<nowiki>[[2]]</nowiki>*t + launchpos<nowiki>[[2]]</nowiki>) /. T, 0} | |||
(* This gives 2 answers, the user must determine which is useful: if yinit = 0, one will be at t=0, if yinit >0, one will be at t <0, if yinit < 0, both will be at t>0, so in the last case | |||
you need to think about the situation*)</code> | |||
<!-- The <nowiki></nowiki> tags are necessary because Stephen Wolfram is apparently too smart to use conventional formatting, so Mathematica uses double brackets for indexing. Mathematica has many, many, idiosyncrasies such as this --> | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
===1. (Simple)=== | |||
A ball leaves a table which is <math> 1.5 \; m </math> high with a horizontal velocity of <math> 2.5 \; \frac{m}{s} </math>. What is the duration of the flight, and what is the horizontal distance it will travel over this time? | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:1200px; overflow:auto;"> | |||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Solution</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
[[File:Npl6.jpg]] | |||
</div></div> | |||
===2. (Middling)=== | |||
A cannon fires a <math> 10 \; kg </math> projectile with <math> 20,000 \; N </math> of force over a duration of <math> 0.1 \; s </math>. The cannon may be fired at angles of <math> 30^\circ, 60^\circ, </math> and <math> 90^\circ </math>. What is the distance the projectile will follow at each of these angles? Which angle will lead to the furthest distance of travel? | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:1200px; overflow:auto;"> | |||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Solution</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
[[File:Npl7.jpg]] | |||
</div></div> | |||
In the example above, the time of flight of each cannonball is determined by finding the time until its highest point and doubling that. This is possible because for this problem the ground is flat; if the cannonball ends up higher or lower than it starts, the time of flight will have to be found using its y-coordinate as a function of time. Once the time of flight is found, it is multiplied by the x component of its velocity to find its horizontal displacement. | |||
===3. (Difficult)=== | |||
The largest snowstorm in a century has come through Atlanta, and you and your friends have decided to have an extremely elaborate snowball fight. You each have constructed snow fort walls 3 meters high (there was a lot of snow), separated by a distance of 20 meters. Now you need to launch your snowball (from a spring loaded cannon, of course) in a perfect parabolic arc in order to hit a target on the ground, exactly two meters behind your friend's snow fort walls. Your cannon is, in turn, exactly two meters behind your wall. Neglecting air resistance, find the angle and launch speed which will allow you to just barely clear the wall, then hit the target on the ground (in other words, the trajectory will have two known points, one at the top point of the wall, and one at the target). | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:1200px; overflow:auto;"> | |||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Solution</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
Since this problem is somewhat tricky, especially in the algebra, the original solution process is attached, along with the set of checks to ensure that the answer is correct. | |||
[[File:projmot diffex 1.jpg]] | |||
[[File:projmot diffex 2.jpg]] | |||
[[File:projmot diffex 3.jpg]] | |||
</div></div> | |||
===4. (Bonus)=== | |||
As a challenge, determine the angle at which the distance traveled by a projectile shot with a fixed velocity will be maximized, and prove that this is the maximum. Assume that the initial and final height will be the same. Hint: find the range of the projectile as a function of the launch angle, then use optimization (find the angle at which the derivative of this function with respect to the angle is equal to zero). | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px; overflow:auto;"> | |||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Solution</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
We can treat <math> y_f = y_i = 0 </math>, so that | |||
<math> 0 = 0 + v_0 \sin(\theta) t_f - \frac{g t_f^2}{2} </math> | |||
<math> x_f = v_0 \cos(\theta) t_f </math> | |||
Then we can solve for <math> t_f </math> | |||
<math> t_f = \frac{2v_0 \sin(\theta)}{g} </math> | |||
and substitute this in to <math> x_f </math> to arrive at | |||
<math> x_f = \frac{2v_0^2 \sin(\theta)\cos(\theta)}{g} = \frac{v_0^2\sin(2\theta)}{g} </math> | |||
Now we optimize the solution, finding that | |||
<math> \frac{\text{d}x}{\text{d}\theta} = 0 = \frac{2v_0^2\cos(2\theta)}{g} </math> | |||
This allows us to solve for <math> \theta </math> and conclude that | |||
<math> \theta = \frac{\pi}{4} </math> | |||
We may check that this is indeed maximization, calculating that | |||
<math> \frac{\text{d}^2x}{\text{d}\theta^2} = - \frac{4v_0^2\sin(2\theta)}{g} </math> | |||
then plugging <math> \theta = \pi/4 </math> to arrive at | |||
<math> \frac{\text{d}^2x}{\text{d}\theta^2}\biggr{|}_{\theta = \pi/4} = -\frac{4v_0^2}{g} </math> | |||
Since this is strictly negative, we know that this point is a maximum, which means that <math> \theta = \pi/4 = 45^{\circ} </math> is the angle at which the projectile will travel a maximum distance. | |||
</div></div> | |||
<b>Additional examples of projectile motion can be found on the [[Kinematics]] page.</b> | |||
<!-- | |||
===Simple=== | ===Simple=== | ||
A ball of mass <math> m = 1000 \; g </math> rolls across the floor with a velocity of <math> \vec{v} = (3,4,0) \;m/s </math> . After how much time does the ball stop? Where does it stop if it starts at the origin? Assume the coefficient of friction is 0.3. | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px; overflow:auto;"> | |||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Solution</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
We need to find when the velocity will be equal to zero, given a constant frictional force | |||
'''Declare known variables and coordinate system:''' | |||
First, we convert mass into kilograms | |||
<math> \mathbf{m} = \frac{1000} {1000} = 1 kg </math> | |||
Next, we restate the velocity and coefficient of friction | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{v}} = (3,4,0) \; \frac{m} {s} </math> | |||
<math> \mu = .3 </math> | |||
Next, from the context of the problem, we take x and y to be perpendicular to the force of gravity (that is, the floor is flat), so gravity will be directed in the negative z direction. | |||
'''Find the initial momentum:''' | |||
<math> \vec{p}_{i} = \mathbf{m} \vec{\mathbf{v}} = (1 \; kg)((3,4,0) \frac{m}{s}) = (3,4,0) \; \frac{kg \; m}{s}</math> | |||
'''Find time passed:''' | |||
We have the momentum principle: | |||
<math> \Delta{\vec{p}} = \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{net} \Delta t </math> | |||
Next, we compute the force due to friction (see [[Friction]]): | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{frict} = \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{N}\cdot\mu </math> | |||
Expanding in the coordinate system we defined earlier: | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{normal} = (0,0,\mathbf{m}|\mathbf{g}|) = (0,0,9.8) N </math> | |||
Now we compute friction. Friction will always be directed in the opposite direction of the velocity, so just as velocity has vector for <math> \vec{\mathbf{v}} = (3,4,0) \; m/s </math>, friction will have vector form <math> \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{frict} = |\vec{\mathbf{F}}_{frict}|(-3/5,-4/5,0) </math>, where <math> |\vec{\mathbf{F}}_{frict}| </math> is the magnitude of the frictional force, and the vector has been normalized, so that its magnitude is equal to one (you should recognize 3,4, and 5 as a Pythagorean triple). Therefore, we calculate | |||
<math> |\vec{\mathbf{F}}_{frict}| = \mu |\vec{\mathbf{F}}_{normal}| = 2.94 \;N </math> | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{frict} = (2.94 \; N)(-3/5,-4/5,0) = (-1.764,-2.352,0) \; N </math> | |||
Now, we compute the time it takes to stop based on the change in momentum | |||
<math> \Delta \vec{p} = \vec{p}_{i} = (\Delta t)\vec{\mathbf{f}}_{frict} </math> | |||
Since the final momentum will be 0, the change in momentum is simply <math> \Delta \vec{\mathbf{p}} = - \vec{\mathbf{p}}_i </math>, so we have | |||
<math> (-3,-4,0) = (-1.764,-2.352,0) N \cdot \Delta {t} </math> | |||
<math> \Delta {t} = \frac {(3,-4.,0) \; kg \; m/s} {(-1.764,-2.352,0) \; N} </math> | |||
<math> \Delta {t} = 1.7 s </math> | |||
'''Find displacement''' | |||
We have two options. We may use average velocity: | |||
<math> \Delta {d} = \vec{v}_{avg} \cdot \Delta {t} = \frac {(3,4,0)} {2} \frac{m} {s} \cdot 1.7 s = (2.55,3.4,0) m </math> | |||
and then find the final position: | |||
<math> \mathbf{r}_{f} = \mathbf{r}_{i} + \Delta {d} = (0,0,0) m + (2.55,3.4,0) m = (2.55, 3.4,0) m</math> | |||
Alternatively, we may use the kinematics equation | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{r}}_f = \frac{\vec{\mathbf{a}} t^2}{2} + \vec{\mathbf{v}}_i t + \vec{\mathbf{r}}_i </math> | |||
where acceleration <math> \vec{a} = \vec{\mathbf{F}}/\mathbf{m} = (-1.764, -2.352, 0) m/s^2 </math>. Thus this yields | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{r}}_f = \frac{(-1.764, -2.352, 0)(1.7 \; s)^2}{2} + (3,4,0)(1.7 \; s) + (0,0,0) = (2.55, 3.4, 0) \; m </math> | |||
</div></div> | |||
===Middling=== | ===Middling=== | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:900px; overflow:auto;"> | |||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Solution</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
You kick a <math>5 \;kg </math> ball off a <math>100\;m</math> cliff at a velocity of <math> (10,15,10)\; m/s </math>. Assume gravity acts in the negative z direction, and that there is no air resistance. How long does it take for the ball to reach the ground? How far away does it land? | |||
'''Declare Known Variables''' | |||
First we have mass <math> \mathbf{m} = 5\; kg </math>. Next, we know that <math> \mathbf{h} = 100\; m </math>, which may be written as <math> \vec{\mathbf{r}}_i = (0,0,100)\; m </math>. fly, we have <math> \vec{\mathbf{v}}_{i} = (10,15,10) \;\frac{m} {s} </math>. | |||
'''Find Initial Momentum''' | |||
Using the definition of [[Linear Momentum]], we find that | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{p}}_{i} = \mathbf{m} \vec{\mathbf{v}}_{i} </math> | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{p}}_{i} = (5\;kg) (10,15,10) \;\frac{m} {s} = (50,75,50) \; \frac{kg \; m} {s}</math> | |||
'''Find Net Force''' | |||
Because gravity is directed in the z-direction, the force will have only a z-component, which we may calculate: | |||
<math> \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{net} = \vec{\mathbf{F}}_{g} = (0,\mathbf{m}\mathbf{g},0) = (0, (5\;kg)(9.8 \;\frac{m} {s^2}),0) = (0,49,0)\; N</math> | |||
'''Find time passed''' | |||
We know that the final z coordinate of the ball will be equal to zero, so we compute the duration of the flight by calculating when this will occur. To do this we use kinematics: | |||
<math> z_f = \frac{1}{2} a_z t^2 + v_z t + z_i </math> | |||
<math> 0 = \frac{1}{2} (-9.8 \; \frac{m}{s^2})t^2 + (10 \; \frac{m}{s})t + 100 \; m </math> | |||
This is a standard quadratic equation, so we can use the quadratic formula to find that: | |||
<math> t = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a} = \frac{ -10 \; \frac{m}{s} \pm \sqrt{100 \; \frac{m^2}{s^2} + 1960 \frac{m^2}{s^2}}}{-9.8 \; \frac{m}{s^2}} </math> | |||
Notice the negative denominator, so it is the minus option that will be positive. Since negative times are unphysical, we discard the plus case and have that <math> t \approx 5.65 s </math>. | |||
'''Find Displacement in x''' | |||
Since no force acts in this direction, it is very straightforward to compute that | |||
<math> x_f = x_i + v_x t</math> | |||
<math> x_f = 0 + (10 \; \frac{m}{s})(5.65 \; s) = 56.5 \; m </math> | |||
'''Find Displacement in y''' | |||
As with above, we may compute | |||
<math> y_f = y_i + v_y t</math> | |||
<math> y_f = 0 + (15 \; \frac{m}{s})(5.65 \; s) = 84.75 \; m</math> | |||
Combining all this, the ball's final position will be <math> (56.5,84,75,0) \; m </math> | |||
</div></div> | |||
===Difficult=== | ===Difficult=== | ||
You kick a ball through 5 meter high posts from 60 meters away. It takes 2.5s to travel through the posts. Answer the following questions: | |||
a)What is the initial velocity? | |||
b)What angle did you shoot it from? | |||
c)What is the velocity of the ball as it crosses the posts? | |||
d)What was the ball's maximum height? | |||
e)What was the force on the ball if the ball is .76 kg and the impact lasts for 34 ms? | |||
====Part A==== | |||
'''Find Initial Velocity in X direction''' | |||
<math> \frac{\Delta {p}_x} {\Delta {t}} = \mathbf{F}_{net} = 0 </math> | |||
<math> \frac{m \cdot\Delta {v}_x} {\Delta {t}} = 0 </math> | |||
Or the x component of the velocity is constant. | |||
<math> \overrightarrow{v}_x = \frac{\Delta {x}} {\Delta {t}} = \frac{60} {2.5} = 24 \frac{m}{s} </math> | |||
'''Find Initial Velocity in Y direction''' | |||
<math> \frac{\Delta {p}_y} {\Delta {t}} = \mathbf{F}_{net} = - \mathbf{m}\mathbf{g} = \frac{m \cdot\Delta {v}_y} {\Delta {t}} </math> | |||
<math> \frac{\Delta {v}_y} {\Delta {t}} = -\mathbf{g}</math> | |||
<math> \Delta {v}_y = - \mathbf{g} \cdot \Delta {t} = v_{final y} - v_{initial y}</math> | |||
<math> v_{final y} = - \mathbf{g} \cdot \Delta {t} + v_{initial y}</math> | |||
<math> v_{avg y} = \frac{v_{final y} + v_{initial y}} {2} </math> | |||
<math> v_{final y} = 2v_{avg y} - v_{initial y} </math> | |||
<math>- \mathbf{g} \cdot \Delta {t} + v_{initial y} = 2v_{avg y} - v_{initial y} </math> | |||
<math> v_{avg y} = v_{initial y} - \frac{1} {2} \mathbf{g} \Delta {t} </math> | |||
<math> \frac{\Delta {y}} {\Delta {t}} = v_{avg y} </math> | |||
<math> \Delta {y} = v_{initial y} \Delta {t} - \frac{1} {2} \mathbf{g} \Delta {t}^2</math> | |||
<math> v_{initial y} = \frac{\Delta {y}} {\Delta {t}} + \frac{1} {2} \mathbf{g} \Delta {t} = \frac{5} {2.5} + \frac{1} {2} \cdot 9.8 \cdot 2.5 = 14.25 \frac {m} {s} </math> | |||
'''Find Initial Velocity in Z direction''' | |||
No change in Z direction, therefore: | |||
<math> v_{initial z} = 0 \frac{m} {s} </math> | |||
'''Find Initial Velocity''' | |||
<math> \overrightarrow{v}_{initial} = (24,14.25,0) \frac {m} {s}</math> | |||
====Part B==== | |||
'''Find the Angle''' | |||
<math> \tan {\theta} = \frac{\mathbf{v_{initial y}}} {\mathbf{v_{initial x}}} = \frac{14.25} {24} = 0.59375</math> | |||
<math> \theta = \tan^{-1} 0.59375 = 0.53358 radians</math> or 30.6997 degrees | |||
====Part C==== | |||
'''Find Final Velocities''' | |||
Final velocity is equal to the velocity as it goes through the poles. | |||
No change in x velocity: | |||
<math> v_{final x} = 24 \frac{m} {s} </math> | |||
From part A: | |||
<math> v_{final y} = - \mathbf{g} \cdot \Delta {t} + v_{initial y}</math> | |||
<math> v_{final y} = - 9.8 \cdot 2.5 + 14.25</math> | |||
<math> v_{final y} = - 10.25 \frac{m} {s}</math> | |||
<math>\overrightarrow{v}_{final} = (24, -10.25, 0) \frac{m} {s}</math> | |||
====Part D==== | |||
'''Find Max Time''' | |||
The velocity at the max point is 0. Use the equation from part A: | |||
<math> v_{max y} = v_{initial y} - g \Delta{t_{max}} = 0</math> | |||
<math>v_{initial y} = g \Delta{t_{max}}</math> | |||
<math>\Delta{t_{max}} = \frac{v_{initial y}} {g}</math> | |||
'''Find Max Height''' | |||
<math> \frac{\Delta {y}} {\Delta{t}} = v_{initial y} - \frac{1}{2} g \Delta{t_{max}}</math> | |||
<math> y_{max} - y_{initial} = v_{initial y} \Delta{t_{max}} - \frac{1}{2} g \Delta{t_{max}}^2</math> | |||
<math> y_{max} = \frac{v_{initial y}^2} {g} - \frac{1}{2} {(\frac{v_{initial y}^2} {g})}</math> | |||
<math> y_{max} = \frac{1}{2} {(\frac{v_{initial y}^2} {g})} = \frac{1}{2} {(\frac{14.25^2} {9.8})} = 10.3603 m</math> | |||
====Part E==== | |||
'''State Known Variables''' | |||
<math> \mathbf{m} = 0.76 kg </math> | |||
<math> \Delta{t} = .034 s </math> | |||
'''Find Change in Momentum''' | |||
<math> \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{initial} = 0 </math> | |||
<math> \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{final} = m \cdot \overrightarrow{v}_{initial} </math> | |||
Use V Initial from Part A: | |||
<math> \Delta{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}} = \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{final} - \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{initial} = m \cdot \overrightarrow{v}_{initial} - 0 = 0.76 kg \cdot (24,14.25,0) \frac{m} {s} = (18.24,10.83,0) kg \frac{m} {s}</math> | |||
<math> |\Delta{\mathbf{p}}| = \sqrt{18.24^2 + 10.83^2} = 21.213 kg \frac{m} {s}</math> | |||
'''Find Net Force''' | |||
<math> |\Delta{\mathbf{p}}| = |\mathbf{F}_{net}| \cdot \Delta{t} </math> | |||
<math> |\mathbf{F}_{net}| = \frac{|\Delta{\mathbf{p}}|} {\Delta{t}} = \frac{21.213} {.034} = 623.908 N</math> | |||
--> | |||
==Connectedness== | ==Connectedness== | ||
Projectile motion has many applications in day-to-day life; every dropped, thrown, and launched object massive enough to disregard air friction is an example of projectile motion. | |||
===Application: rifle scope industry=== | |||
A bullet fired from a horizontal hunting rifle obeys the model of projectile motion, so by the time it reaches a given horizontal distance from the hunter, it will have fallen vertically by a predictable amount. The scope of a hunting rifle can be calibrated to specific distances. This angles the scope slightly below the horizontal to take into account the bullet drop; when the bullet reaches the horizontal distance of interest, it will have fallen exactly into the crosshair of the scope. The design and manufacture of the scopes and their calibration mechanisms require a quantitative understanding of projectile motion. | |||
===Application: sports=== | |||
In most physical sports, such as basketball, soccer, football, and tennis, projectile motion principles are employed extensively by players. For instance, basketball players utilize an understanding of projectile motion to accurately shoot the ball from different distances and angles, considering initial velocity and launch angle. Similarly, in soccer and football, players aim for their target by kicking or throwing the ball with precise velocity and angle with consideration of gravity and other forces acting on the ball. Thus, an intuitive understanding of projectile motion enhances players' abilities to predict the path of the ball and make strategic decisions during gameplay. | |||
===Application: shot put=== | |||
Shot put is another such sport and a prime demonstration of fundamental projectile motion. In standard competitions, a shot put is 16lbs for men and 8.8lbs for women. Due to the large density of the ball and low velocity when thrown, air resistance minimally affects the trajectory of the path. The thrower must consider the height at launch, since the ball's landing height is lower, relatively. Thus, a 45 degree angle may not lead to an optimal throw. In practice, for most skilled shot putters, the optimal angle of release tends to be slightly below this. Since the starting height is above the landing height, throwers may put more forward velocity into their throws to achieve a greater horizontal distance! | |||
[[File:Shotput.png|right]] | |||
===Application: cannonball firing=== | |||
Firing a cannonball serves as a classic example of projectile motion, demonstrating the principles of physics involved in the trajectory of a launched object. The cannonball is first propelled with an initial velocity determined by the force of the explosion from within the cannon. The angle at which the cannon is aimed affects the trajectory of the cannonball. In the air, gravity pulls the cannonball downward while it follows a parabolic path. Air resistance, typically negligible over short distances, may influence its trajectory at high speeds or long distances. | |||
===Application: fireworks=== | |||
The design of fireworks displays rely heavily on the principles of projectile motion. Pyrotechnic engineers must use these principles to plan each firework's trajectory upon deployment, ensuring they explode at the desired height and location in the sky by taking into account gravity. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
The history of projectile motion is closely entwined with the history of [[Kinematics]], and so in many ways, the history of one is the history of the other. A few special notes may be made about projectiles though. Aristotle was one of the first to write extensively about the motion of objects and made a number of claims. First, he argued that heavy objects (like stones) fall because they are made primarily of earth, which is attracted to other earth, whereas smoke rises because it is made of air, and is attracted to other air. <ref>http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~blackman/ast104/aristotle_dynamics13.html </ref> He also believed that objects move only due to propelling forces, leading him to conclude that the air itself pushes objects forward, through some form of vacuum interaction. <ref> http://galileo.rice.edu/lib/student_work/experiment95/paraintr.html </ref> <ref> http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~blackman/ast104/aristotle_dynamics13.html </ref> | |||
It was Galileo who recognized the flaws in this argument, and who instead put forth the idea of inertia, that objects will ''stay'' in motion unless acted upon by outside forces. <ref> http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/211.fall2000.web.projects/J.%20Gentry%20and%20D.%20Arnold/phys211.html </ref> Galileo also identified the parabolic arcs characteristic of projectile motion.<ref> http://www.mcm.edu/academic/galileo/ars/arshtml/mathofmotion2.html </ref> He did this, and identified the separability of the horizontal and vertical motion, by rolling balls off of inclined planes and then over a ledge, and noting the resultant trajectories. | |||
== | These developments were formalized and given greater detail by Newton, who explained them and many other phenomena through his laws and the development of appropriate mathematical techniques.<ref> https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/principia-mathematica/ </ref> In addition to his three laws, the law of universal gravitation also connected the gravity we experience on Earth with the force that drives the motions of orbital objects, although this motion is substantially more complicated than our simple projectile model. | ||
<!-- | |||
Several important figures have contributed to the modern understanding of projectile motion. | |||
===Aristotle=== | |||
The first findings of Projectile Motion were contributed by Aristotle. He believed that a projectile modeled by a canon ball travels in a straight line until it lost its 'impetus'. When it lost its 'impetus' which ran out over time, due to a restive force, the projectile would immediately drop and fall to the ground. For objects projected over short distances, at first observation this can visually appear to be true. | |||
===Galileo=== | |||
Galileo's findings were motivated by the Renaissance. Through a series of experiments, he discovered that projectile motion is a result of free fall motion along the y-axis and uniform (constant velocity) motion along the x-axis. This model became well-known and led to new insights into projectile motion, such as its parabolic shape. It is still accepted today. | |||
One experiment Galileo performed in developing this model consisted of dropping two objects from equal heights: one from rest, and one with an initial horizontal velocity. Both struck the ground at the same time because both had the same initial vertical velocity. The horizontal component of velocity does not affect its vertical motion because the components of motion are independent. | |||
===Isaac Newton=== | |||
Isaac Newton contributed to the idea of projectile motion with his idea of a cannon on a mountaintop, now known as Newton's cannonball. Newton hypothesized that a cannon on top of a high mountain could fire a ball with varying initial speeds for varying trajectories. A cannonball simply dropped off the mountain would merely return to earth, but if that cannonball were fired from a cannon then it would return to Earth in an arc or parabolic shape. This would be considered projectile motion. Neither of these scenarios was new or particularly innovative, but Newton also imagined a third scenario in which the cannonball was launched at great speed. In this scenario, he imagined that the ball would travel so far before curving downward that the earth would curve underneath it due to its spherical shape, resulting in a circular orbit. In doing so, Isaac Newton became one of the first to imagine universal gravity and to come up with a cause for orbital motion. It is worth noting that Newton's contribution does not strictly fall under the category of projectile motion as it is defined on this page because, in the case of a cannonball orbiting the earth, gravity is not constant and downward, but changes its direction depending on the cannonball's position to point towards the center of the earth. | |||
--> | |||
== See also == | |||
*[[Kinematics]] | |||
*[[Velocity]] | |||
*[[Acceleration]] | |||
*[[Frame of Reference]] | |||
*[[Iterative Prediction]] | |||
*[[Terminal Speed]] | |||
===External links=== | ===External links=== | ||
*[http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Vectors-and-Projectiles/Projectile-Simulator Interactive Projectile Simulator] | |||
===Further Reading=== | |||
Matter and Interactions, 4th Edition | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Interactions]] | |||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 17:29, 21 April 2024
Edited by YorickAndeweg June 2019
Edited by Richard Udall July 2019
Edited by Sarah Kilgore November 2022
Edited by Audrey Cho April 2024
Motion in which an object is affected only by the constant force of gravity is referred to as projectile motion (and the object as a projectile). This scenario is necessarily a simplification, since one larger scales gravity is not constant as one moves away from the attracting object, and there is also usually air resistance acting upon the object. However, it is a useful approximation, and an instructive use of kinematics.
The Main Idea
Projectile motion is a branch of classical mechanics which analyzes the motion of objects (projectiles) under the influence of the constant acceleration of gravity near the surface of the earth.[1] Often, the projectiles are propelled prior to being analyzed under the influence of gravity, giving them initial velocities that affect their trajectories. Two classic examples of projectile motion are the firing of a cannon and throwing a ball off a tower. An object is a projectile if it is subject only to the constant force of gravity. For real projectiles, other forces such as air resistance are usually present, but these make the mathematical model significantly more complicated, and fair estimations may be gotten when disregarding them for many cases (note, however, that the relative importance of these forces increases for a feather vs for a ball). Regardless of the direction of motion of the projectile, the free-body diagram of a projectile is always the same, and constant throughout its trajectory: a particle on which only gravity acts in a downward direction.
Properties
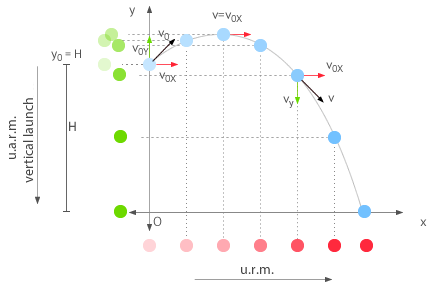
1. Motion is considered parabolic.
2. Horizontal component of acceleration is considered to be zero.
3. Vertical component of acceleration is constant because of gravity.
4. Horizontal and Vertical motion components are independent but share the same time.
A Mathematical Model
Traditionally, the Frame of Reference chosen for projectile motion problems places the origin on the ground below the point of launch and defines t=0 to be the time of launch.The +y direction is usually defined as vertically upwards, so the gravitational force acts in the -y direction. Because there will be no forces horizontal to the ground, it is possible to define our coordinate system with the +x direction as the direction of the horizontal component of the projectile's velocity, and in doing so ignore the third dimension altogether. The y component of the velocity is constantly changing over time due to the gravitational force. Gravity near the surface of the earth causes a constant downward acceleration of 9.8m/s^2. This causes a parabolic trajectory. The constant velocity in the x direction and the constant acceleration in the y direction lend themselves to the Kinematic Equations. Kinematics are used to analytically solve problems related to projectile motion.
The following equations derived from kinematics describe the x and y components of a projectile's position as functions of time.[2]
[math]\displaystyle{ y(t) = - \frac{1}{2} g \cdot t^2 + v_{y, 0} \cdot t + y_i }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ x(t) = v_{x, 0} \cdot t }[/math]
It is evident from the above equations that the two components of a projectile's motion are independent; the particle's horizontal position has no effect on its vertical motion and vice versa.
[math]\displaystyle{ v_{y, 0} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ v_{y, 0} }[/math] may each be positive, negative, or 0, depending on how the projectile was launched, resulting in a variety of trajectory shapes. Below are some possible trajectories of projectiles:
Note that all of these shapes are parabolic.
Sometimes, an initial speed and an initial angle (usually with respect to the horizontal) is given. In this case, [math]\displaystyle{ v_{y, 0} = v_0 \sin \theta_0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ v_{x, 0} = v_0 \cos \theta_0 }[/math].
Sometimes, rather than giving an initial velocity, a projectile motion problem will give the mass of the projectile as well as the magnitude, direction, and duration of the propelling force launching it. From this information, the relationship between Impulse and Momentum can be used to find the initial velocity of the projectile. In these situations, the propelling force is usually considered the only force acting on the object during the pre-trajectory impulse, because even if other forces are present, they are usually negligible compared to the propelling force.
At the highest point in a projectile's trajectory, the projectile's velocity is entirely horizontal; the vertical component is 0. This is because at that point in time, the vertical velocity has stopped being positive and is no longer carrying the projectile higher, but has not yet become negative and has therefore not begun lowering the projectile once more.
A Computational Model
One method used to visualize or predict a projectiles trajectory is to apply our mathematical model using computational programming. Computer models usually use Iterative Prediction rather than Kinematics to determine the path of the projectile. Here is an example of a program in vPython that simulates a projectile:
Click "view this program" on the top left corner to view the source code.
When working with algebraic solutions such as this one, one may also make use of analytic solution engines such as Mathematica or Maple. The same snippet of code describing projectile motion is used here and in Kinematics:
(*First Cell*)
(*Setup for a generic projectile motion problem*)
launchspeed = 10
launchangle = Pi/6
vinit = launchspeed*{Cos[launchangle], Sin[launchangle], 0}
launchpos = {0, 0, 0}
yterminus = 0
g = 9.8
Naturally, one can edit these values to set up a different problem. The setup and the equation solution itself is separated into two cells (Mathematica has a cell notebook based structure) for cleanliness' sake.
(*Second Cell*)
(*Solving for the time of impact, then plugging that in to the original equations to find position in x and y *)
T = Solve[-g*t^2/2 + vinit[[2]]*t + launchpos[[2]] == yterminus, t]
finalpos = {(vinit[[1]]*t + launchpos[[1]]) /. T, (-g*t^2/2 + vinit[[2]]*t + launchpos[[2]]) /. T, 0}
(* This gives 2 answers, the user must determine which is useful: if yinit = 0, one will be at t=0, if yinit >0, one will be at t <0, if yinit < 0, both will be at t>0, so in the last case
you need to think about the situation*)
Examples
1. (Simple)
A ball leaves a table which is [math]\displaystyle{ 1.5 \; m }[/math] high with a horizontal velocity of [math]\displaystyle{ 2.5 \; \frac{m}{s} }[/math]. What is the duration of the flight, and what is the horizontal distance it will travel over this time?
2. (Middling)
A cannon fires a [math]\displaystyle{ 10 \; kg }[/math] projectile with [math]\displaystyle{ 20,000 \; N }[/math] of force over a duration of [math]\displaystyle{ 0.1 \; s }[/math]. The cannon may be fired at angles of [math]\displaystyle{ 30^\circ, 60^\circ, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ 90^\circ }[/math]. What is the distance the projectile will follow at each of these angles? Which angle will lead to the furthest distance of travel?
In the example above, the time of flight of each cannonball is determined by finding the time until its highest point and doubling that. This is possible because for this problem the ground is flat; if the cannonball ends up higher or lower than it starts, the time of flight will have to be found using its y-coordinate as a function of time. Once the time of flight is found, it is multiplied by the x component of its velocity to find its horizontal displacement.
3. (Difficult)
The largest snowstorm in a century has come through Atlanta, and you and your friends have decided to have an extremely elaborate snowball fight. You each have constructed snow fort walls 3 meters high (there was a lot of snow), separated by a distance of 20 meters. Now you need to launch your snowball (from a spring loaded cannon, of course) in a perfect parabolic arc in order to hit a target on the ground, exactly two meters behind your friend's snow fort walls. Your cannon is, in turn, exactly two meters behind your wall. Neglecting air resistance, find the angle and launch speed which will allow you to just barely clear the wall, then hit the target on the ground (in other words, the trajectory will have two known points, one at the top point of the wall, and one at the target).
4. (Bonus)
As a challenge, determine the angle at which the distance traveled by a projectile shot with a fixed velocity will be maximized, and prove that this is the maximum. Assume that the initial and final height will be the same. Hint: find the range of the projectile as a function of the launch angle, then use optimization (find the angle at which the derivative of this function with respect to the angle is equal to zero).
We can treat [math]\displaystyle{ y_f = y_i = 0 }[/math], so that
[math]\displaystyle{ 0 = 0 + v_0 \sin(\theta) t_f - \frac{g t_f^2}{2} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ x_f = v_0 \cos(\theta) t_f }[/math]
Then we can solve for [math]\displaystyle{ t_f }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ t_f = \frac{2v_0 \sin(\theta)}{g} }[/math]
and substitute this in to [math]\displaystyle{ x_f }[/math] to arrive at
[math]\displaystyle{ x_f = \frac{2v_0^2 \sin(\theta)\cos(\theta)}{g} = \frac{v_0^2\sin(2\theta)}{g} }[/math]
Now we optimize the solution, finding that
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\text{d}x}{\text{d}\theta} = 0 = \frac{2v_0^2\cos(2\theta)}{g} }[/math]
This allows us to solve for [math]\displaystyle{ \theta }[/math] and conclude that
[math]\displaystyle{ \theta = \frac{\pi}{4} }[/math]
We may check that this is indeed maximization, calculating that
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\text{d}^2x}{\text{d}\theta^2} = - \frac{4v_0^2\sin(2\theta)}{g} }[/math]
then plugging [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = \pi/4 }[/math] to arrive at
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\text{d}^2x}{\text{d}\theta^2}\biggr{|}_{\theta = \pi/4} = -\frac{4v_0^2}{g} }[/math]
Since this is strictly negative, we know that this point is a maximum, which means that [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = \pi/4 = 45^{\circ} }[/math] is the angle at which the projectile will travel a maximum distance.
Additional examples of projectile motion can be found on the Kinematics page.
Connectedness
Projectile motion has many applications in day-to-day life; every dropped, thrown, and launched object massive enough to disregard air friction is an example of projectile motion.
Application: rifle scope industry
A bullet fired from a horizontal hunting rifle obeys the model of projectile motion, so by the time it reaches a given horizontal distance from the hunter, it will have fallen vertically by a predictable amount. The scope of a hunting rifle can be calibrated to specific distances. This angles the scope slightly below the horizontal to take into account the bullet drop; when the bullet reaches the horizontal distance of interest, it will have fallen exactly into the crosshair of the scope. The design and manufacture of the scopes and their calibration mechanisms require a quantitative understanding of projectile motion.
Application: sports
In most physical sports, such as basketball, soccer, football, and tennis, projectile motion principles are employed extensively by players. For instance, basketball players utilize an understanding of projectile motion to accurately shoot the ball from different distances and angles, considering initial velocity and launch angle. Similarly, in soccer and football, players aim for their target by kicking or throwing the ball with precise velocity and angle with consideration of gravity and other forces acting on the ball. Thus, an intuitive understanding of projectile motion enhances players' abilities to predict the path of the ball and make strategic decisions during gameplay.
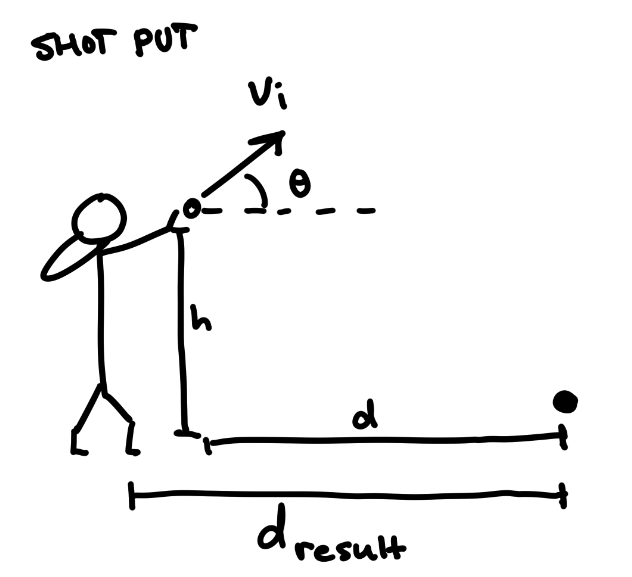
Application: shot put
Shot put is another such sport and a prime demonstration of fundamental projectile motion. In standard competitions, a shot put is 16lbs for men and 8.8lbs for women. Due to the large density of the ball and low velocity when thrown, air resistance minimally affects the trajectory of the path. The thrower must consider the height at launch, since the ball's landing height is lower, relatively. Thus, a 45 degree angle may not lead to an optimal throw. In practice, for most skilled shot putters, the optimal angle of release tends to be slightly below this. Since the starting height is above the landing height, throwers may put more forward velocity into their throws to achieve a greater horizontal distance!
Application: cannonball firing
Firing a cannonball serves as a classic example of projectile motion, demonstrating the principles of physics involved in the trajectory of a launched object. The cannonball is first propelled with an initial velocity determined by the force of the explosion from within the cannon. The angle at which the cannon is aimed affects the trajectory of the cannonball. In the air, gravity pulls the cannonball downward while it follows a parabolic path. Air resistance, typically negligible over short distances, may influence its trajectory at high speeds or long distances.
Application: fireworks
The design of fireworks displays rely heavily on the principles of projectile motion. Pyrotechnic engineers must use these principles to plan each firework's trajectory upon deployment, ensuring they explode at the desired height and location in the sky by taking into account gravity.
History
The history of projectile motion is closely entwined with the history of Kinematics, and so in many ways, the history of one is the history of the other. A few special notes may be made about projectiles though. Aristotle was one of the first to write extensively about the motion of objects and made a number of claims. First, he argued that heavy objects (like stones) fall because they are made primarily of earth, which is attracted to other earth, whereas smoke rises because it is made of air, and is attracted to other air. [3] He also believed that objects move only due to propelling forces, leading him to conclude that the air itself pushes objects forward, through some form of vacuum interaction. [4] [5]
It was Galileo who recognized the flaws in this argument, and who instead put forth the idea of inertia, that objects will stay in motion unless acted upon by outside forces. [6] Galileo also identified the parabolic arcs characteristic of projectile motion.[7] He did this, and identified the separability of the horizontal and vertical motion, by rolling balls off of inclined planes and then over a ledge, and noting the resultant trajectories.
These developments were formalized and given greater detail by Newton, who explained them and many other phenomena through his laws and the development of appropriate mathematical techniques.[8] In addition to his three laws, the law of universal gravitation also connected the gravity we experience on Earth with the force that drives the motions of orbital objects, although this motion is substantially more complicated than our simple projectile model.
See also
External links
Further Reading
Matter and Interactions, 4th Edition
References
- ↑ https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/Lesson-2/What-is-a-Projectile
- ↑ http://webhome.phy.duke.edu/~rgb/Class/intro_physics_1/intro_physics_1.pdf
- ↑ http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~blackman/ast104/aristotle_dynamics13.html
- ↑ http://galileo.rice.edu/lib/student_work/experiment95/paraintr.html
- ↑ http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~blackman/ast104/aristotle_dynamics13.html
- ↑ http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/211.fall2000.web.projects/J.%20Gentry%20and%20D.%20Arnold/phys211.html
- ↑ http://www.mcm.edu/academic/galileo/ars/arshtml/mathofmotion2.html
- ↑ https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/principia-mathematica/





