Electromagnetic Spectrum: Difference between revisions
Croberts65 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Croberts65 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
===Simple=== | |||
What type of electromagnetic wave has a higher frequency, ultraviolet or infrared? | |||
A. Ultraviolet | |||
=== | ===Middling=== | ||
Calculate the frequency of violet light (450 nm). | Calculate the frequency of violet light (450 nm). | ||
1. <math>450 \times 10^{-9} = \frac {2.998 \times 10^8}{\lambda}</math> | 1. <math>v = {\frac{c}{\lambda}}</math> | ||
2. <math>450 \times 10^{-9} = \frac {2.998 \times 10^8}{\lambda}</math> | |||
3. <math>\frac {1}{\lambda} = \frac {450 \times 10^{-9}}{2.998 \times 10^8} = 1.501 \times 10^{-15}</math> | |||
4. <math>\lambda = 6.662 \times 10^{14}</math> Hz | |||
===Difficult=== | ===Difficult=== | ||
A small laser used as a pointer produces a beam of red light 2 mm in diameter, and has a power output of 4 milliwatts. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the laser beam? | A small laser used as a pointer produces a beam of red light 2 mm in diameter, and has a power output of 4 milliwatts. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the laser beam? | ||
1. <math>E = \sqrt {\frac {4 \times 10^{-3} / (2/2) \times 10^{-3 + -3}}{(2.998 \times 10^{8}) \times ( | 1. <math>E = \sqrt {\frac{P/A}{c \times \epsilon_{0}}}</math> | ||
2. <math>E = \sqrt { \frac{(4 \times 10^{-3}) / ((2/2) \pi \times 10^{-3 + -3})}{(2.998 \times 10^{8}) \times (8.85 \times 10^{-12})} }</math> | |||
3. <math>E = \sqrt { \frac{4 \times 10^{3}}{2.65 \pi \times 10^{-3}} }</math> | |||
4. <math>E = \sqrt {4.80 \times 10^5} = 6.93 \times 10^{2}</math> | |||
==Interaction With Matter== | |||
*Micro Waves - cause forces on molecules that cause torsion and rotation, causing friction in more strongly interconnected molecules, like food and other solids; this is why food heats up in a microwave oven | |||
*Infrared Waves - causes molecular vibration, basically, this is what heat lamps produce, which is why the air gets hot around the lamp | |||
*Visible Light - can produce ionization, but really acts more like infrared waves than ultraviolet waves | |||
*Ultraviolet Waves - causes molecular ionization, but doesn't move the molecule around; this is why you get sunburned, because the ultraviolet light is destroying your skin | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 68: | ||
==Connectedness== | ==Connectedness== | ||
The electromagnetic spectrum is used for a variety of things including | |||
*Cooking (microwaves) | *Cooking (microwaves) | ||
*Radio and Communication | *Radio and Communication | ||
| Line 60: | Line 76: | ||
*Medical Treatments (gamma rays, x-rays) | *Medical Treatments (gamma rays, x-rays) | ||
*Nuclear Physics | *Nuclear Physics | ||
*The sense of sight | |||
==References & Further Reading== | ==References & Further Reading== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:39, 5 December 2015
This page has been created and claimed by Clayton Roberts (Croberts65)
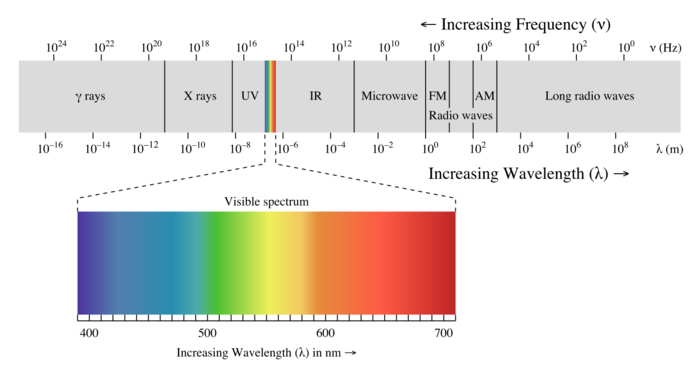
The electromagnetic spectrum describes all different frequencies of light that can be observed, and is most commonly associated with the visible chromatic colors.
The Main Idea
The frequency in Hertz (Hz) of electromagnetic waves can be related to the energy and color (if applicable) of the type of electromagnetic radiation. This can be used in chemistry for ionization, among other fields of science where the material and relative temperature can be related.
A Mathematical Model
[math]\displaystyle{ v = {\frac{c}{\lambda}} }[/math] where
- [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math] is the frequency of the electromagnetic wave in Hertz (Hz) or number of cycles a second and can also be written as "[math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math]"
- [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] is the speed of light ( [math]\displaystyle{ 2.998 \times 10^8 \frac{m}{s} }[/math] )
- [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda }[/math] is the wavelength in meters
[math]\displaystyle{ E = \sqrt {\frac{P/A}{c \times \epsilon_{0}}} }[/math] where
- [math]\displaystyle{ E }[/math] is the magnitude of the electric field in Newtons per Columb (N/C)
- [math]\displaystyle{ P }[/math] is the power output of the beam of electromagnetic waves in Watts (W)
- [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] is the area of the beam in meters squared ( [math]\displaystyle{ m^{2} }[/math] )
- [math]\displaystyle{ \epsilon_{0} }[/math] is the vacuum permittivity constant ( [math]\displaystyle{ 8.85 \times 10^{-12} }[/math] )
- [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] is the speed of light ( [math]\displaystyle{ 2.998 \times 10^8 \frac{m}{s} }[/math] )
A Visual Model
Examples
Simple
What type of electromagnetic wave has a higher frequency, ultraviolet or infrared?
A. Ultraviolet
Middling
Calculate the frequency of violet light (450 nm).
1. [math]\displaystyle{ v = {\frac{c}{\lambda}} }[/math]
2. [math]\displaystyle{ 450 \times 10^{-9} = \frac {2.998 \times 10^8}{\lambda} }[/math]
3. [math]\displaystyle{ \frac {1}{\lambda} = \frac {450 \times 10^{-9}}{2.998 \times 10^8} = 1.501 \times 10^{-15} }[/math]
4. [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda = 6.662 \times 10^{14} }[/math] Hz
Difficult
A small laser used as a pointer produces a beam of red light 2 mm in diameter, and has a power output of 4 milliwatts. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the laser beam?
1. [math]\displaystyle{ E = \sqrt {\frac{P/A}{c \times \epsilon_{0}}} }[/math]
2. [math]\displaystyle{ E = \sqrt { \frac{(4 \times 10^{-3}) / ((2/2) \pi \times 10^{-3 + -3})}{(2.998 \times 10^{8}) \times (8.85 \times 10^{-12})} } }[/math]
3. [math]\displaystyle{ E = \sqrt { \frac{4 \times 10^{3}}{2.65 \pi \times 10^{-3}} } }[/math]
4. [math]\displaystyle{ E = \sqrt {4.80 \times 10^5} = 6.93 \times 10^{2} }[/math]
Interaction With Matter
- Micro Waves - cause forces on molecules that cause torsion and rotation, causing friction in more strongly interconnected molecules, like food and other solids; this is why food heats up in a microwave oven
- Infrared Waves - causes molecular vibration, basically, this is what heat lamps produce, which is why the air gets hot around the lamp
- Visible Light - can produce ionization, but really acts more like infrared waves than ultraviolet waves
- Ultraviolet Waves - causes molecular ionization, but doesn't move the molecule around; this is why you get sunburned, because the ultraviolet light is destroying your skin
History
The first time that a part of the electromagnetic spectrum was observed was in 1800, when scientist William Herschel was looking at light from a heated object through a prism. He noticed that the light surpassed the color red, into what we now know today as the infrared frequency of light. Some years later in 1845, Micheal Faraday made the connection between light and electromagnetism, when he observed that polarized light responded to a magnet. James Maxwell made the final step, when he realized that electromagnetic waves must travel at the speed of light.
Connectedness
The electromagnetic spectrum is used for a variety of things including
- Cooking (microwaves)
- Radio and Communication
- Radar
- Military Defense
- Environmental Impacts (ultraviolet light)
- Medical Treatments (gamma rays, x-rays)
- Nuclear Physics
- The sense of sight