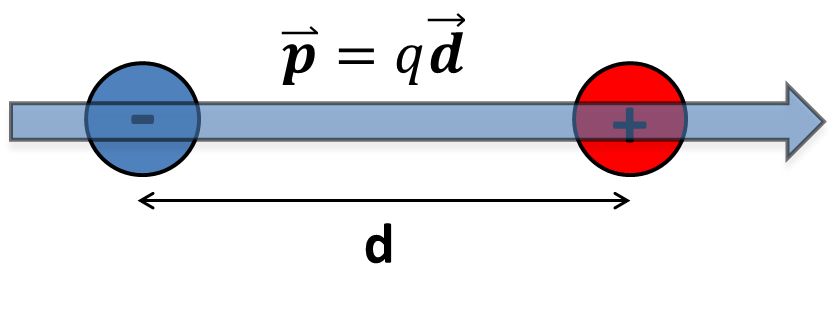Electric Dipole Moment: Difference between revisions
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Created by Summer Mia Bain (Spring 2017) | |||
An electric dipole is created by the combination of two equal and oppositely charged atoms of charge '''q''' that are separated by a a distance ""s"". An electric dipole is the simplest piece of neutral matter that can be analyzed in detail. The size of the dipole is measured by its dipole moment "p" which is a product of its charge "q" and distance "s". The electric dipole moment points from the negative to the positive charge | An electric dipole is created by the combination of two equal and oppositely charged atoms of charge '''q''' that are separated by a a distance ""s"". An electric dipole is the simplest piece of neutral matter that can be analyzed in detail. The size of the dipole is measured by its dipole moment "p" which is a product of its charge "q" and distance "s". The electric dipole moment points from the negative to the positive charge | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==The Main Idea== | ==The Main Idea== | ||
===A Mathematical Model=== | ===A Mathematical Model=== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
<math> \boldsymbol{p} = \boldsymbol{s} \times\mathbf{q}</math> | <math> \boldsymbol{p} = \boldsymbol{s} \times\mathbf{q}</math> | ||
Objects with electric dipole moments are also able to undergo a torque in the presence of electric fields | Objects with electric dipole moments are also able to undergo a torque in the presence of electric fields, which will cause it to rotate | ||
<math> \mathbf{τ} = \boldsymbol{p} \times\mathbf{E}</math> | <math> \mathbf{τ} = \boldsymbol{p} \times\mathbf{E}</math> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
[[File:electricdipolemoment.png]] | |||
This image shows the electric dipole moment, a vector quantity thats expresses the strength of a dipole. Notice how the electric dipole moment goes from the negative charge to the positive charge. | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
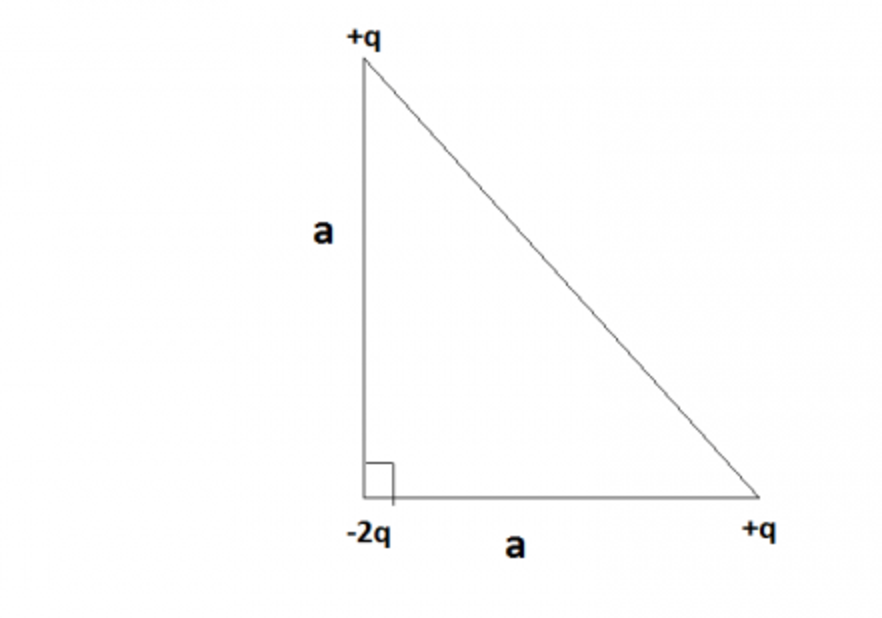
[[File:Simple_DipoleMoment.png]] | [[File:Simple_DipoleMoment.png]] | ||
'''Find the electric dipole moment of this system''' | 1)'''Find the electric dipole moment of this system''' | ||
'''Steps''' | '''Steps''' | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
<math> \boldsymbol{|p|} = \boldsymbol{qa} \displaystyle {\sqrt {2}} </math> | <math> \boldsymbol{|p|} = \boldsymbol{qa} \displaystyle {\sqrt {2}} </math> | ||
2)'''An electric dipoles has a charge of 3.2 * 10^-19C and a separation distance of 0.25 nm. The electric field is 4* 10^6 N/C. It is oriented along the y axis''' | |||
''(a) What is the magnitude and direction of the electric dipole moment?'' | |||
p = qd | |||
= (3.2*10^-19 C) (0.25 * 10^-9) | |||
= 8 * 10^- 29 Cm + j | |||
''(b) What is the force on each charge and the net force of the entire dipole'' | |||
F = qE | |||
= 3.2 * 10^-19C * 4* 10^6 N/C | |||
= 1.28 * 10 ^ -12 N | |||
''(c) What is the magnitude of the net torque?'' | |||
T = PEsin theta | |||
=(8*10^-29)*(4*10^6) sin(90) | |||
= 3.2 * 10 ^-22 Nm | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
[http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/Electric_Dipole Electric Dipole] | |||
[http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/Magnetic_Dipole_Moment Magnetic Dipole Moment] | |||
[http://www.kshitij-iitjee.com/Electric-dipole-in-an-electric-field Electric dipole in an electric field] | |||
===External links=== | ===External links=== | ||
[http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dipole.html Hyper Physics - Electric Dipoles] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_dipole_moment Wikipedia Page] | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_dipole_moment Wikipedia Page] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 2 December 2018
Created by Summer Mia Bain (Spring 2017)
An electric dipole is created by the combination of two equal and oppositely charged atoms of charge q that are separated by a a distance ""s"". An electric dipole is the simplest piece of neutral matter that can be analyzed in detail. The size of the dipole is measured by its dipole moment "p" which is a product of its charge "q" and distance "s". The electric dipole moment points from the negative to the positive charge
The Main Idea
A Mathematical Model
The electric dipole moment is represented by the letter "p". This set is equal to the charge of the atom in an electric dipole multiplied by the distance between the atoms.
[math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol{p} = \boldsymbol{s} \times\mathbf{q} }[/math]
Objects with electric dipole moments are also able to undergo a torque in the presence of electric fields, which will cause it to rotate
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{τ} = \boldsymbol{p} \times\mathbf{E} }[/math]
Note, this multiplication sign here signifies as "cross product"
A Computational Model
This image shows the electric dipole moment, a vector quantity thats expresses the strength of a dipole. Notice how the electric dipole moment goes from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Examples
1)Find the electric dipole moment of this system
Steps
1) Spilt the 2q charge into 2 charges, a positive charge and a negative
2) Notice the geometry of the system, because it has 2 sides of equal length it is a 45-45-90 triangle
3) Solve using the following mathematical equations
[math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol{p}^2 = \boldsymbol{p1}^2 \times\boldsymbol{p2}^2 }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol{|p|} = \displaystyle {\sqrt {{p1}^2 + {p2}^2 }} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol{|p|} = \boldsymbol{qa} \displaystyle {\sqrt {2}} }[/math]
2)An electric dipoles has a charge of 3.2 * 10^-19C and a separation distance of 0.25 nm. The electric field is 4* 10^6 N/C. It is oriented along the y axis
(a) What is the magnitude and direction of the electric dipole moment?
p = qd
= (3.2*10^-19 C) (0.25 * 10^-9) = 8 * 10^- 29 Cm + j
(b) What is the force on each charge and the net force of the entire dipole
F = qE
= 3.2 * 10^-19C * 4* 10^6 N/C = 1.28 * 10 ^ -12 N
(c) What is the magnitude of the net torque?
T = PEsin theta =(8*10^-29)*(4*10^6) sin(90) = 3.2 * 10 ^-22 Nm
See also
Electric dipole in an electric field
External links
Hyper Physics - Electric Dipoles