Johannes Kepler: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:Johannes Kepler 1610.jpg|right|300px|thumb|Johannes Kepler in a 1610 painting]] | [[File:Johannes Kepler 1610.jpg|right|300px|thumb|Johannes Kepler in a 1610 painting]] | ||
== | ==Personal Life== | ||
Johannes Kepler (December 27, 1571 – November 15, 1630). He is an important figure during the scientific revolution of the 17th century. He is most famous for his laws of planetary motion. These laws also help lead to Newton's theory of gravity. | |||
==Laws of Planetary Motion== | ==Laws of Planetary Motion== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
[http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/kepler.html] | [http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/kepler.html] | ||
[http://galileo.rice.edu/sci/kepler.html] | |||
[[Category:Notable Scientists]] | [[Category:Notable Scientists]] | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 3 December 2015
Page Claimed by Davis Johnston

Personal Life
Johannes Kepler (December 27, 1571 – November 15, 1630). He is an important figure during the scientific revolution of the 17th century. He is most famous for his laws of planetary motion. These laws also help lead to Newton's theory of gravity.
Laws of Planetary Motion
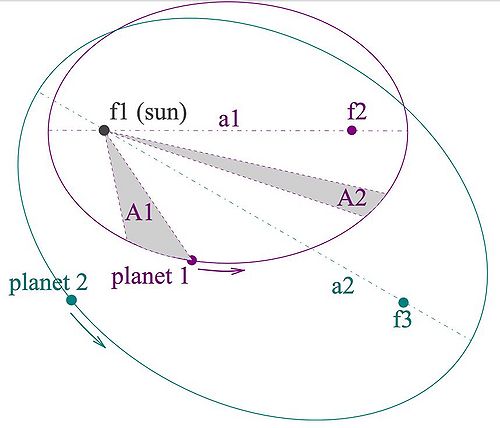
1. Law of Orbits
All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one of the two foci
2. Law of Areas
A line that connects a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
3. Law of Periods
The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi major axis of its orbit.
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic