Thermal Energy: Difference between revisions
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Simple=== | ===Simple=== | ||
500g of water was heated from the initial temperature of 20°C to 50 °C. What is the change in thermal energy of water? (Heat capacity of water is 4.2J/°C*g | 500g of water was heated from the initial temperature of 20°C to 50 °C. What is the change in thermal energy of water? (Heat capacity of water is 4.2J/g*°C) | ||
1. Q = m*C*dT, Q=?, m=500g, C=4.2J/g*°C, dT=T_f-T_i | |||
===Middling=== | ===Middling=== | ||
Revision as of 17:34, 3 December 2015
Work in progress by KwangJun Jung
Thermal energy is energy possessed by an object or system due to the movement of particles within the object or the system.
The Main Idea
All objects are made up of numerous particles or molecules. Within these objects, those particles or molecules are constantly moving or vibrating, generating heat. Thermal energy refers to the internal energy that comes from these moving particles or molecules within the objects. What we mean by a change of "thermal" energy is that part of the internal energy that is associated with a temperature change. In many situations it isn't possible to say how much of the internal energy is thermal, but if the heat capacity is known, we can use a thermometer to measure a change in the thermal energy.
A Mathematical Model
Change in thermal energy can be calculated by using the following mathematical equation. [math]\displaystyle{ {Q = m*C*dT} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ {Q} }[/math] is the thermal energy in Joules, [math]\displaystyle{ {m} }[/math] is the mass of an object in grams, [math]\displaystyle{ {C} }[/math] is the object's specific heat capacity, and [math]\displaystyle{ {dT} }[/math] is the change in object's temperature in Celsius.
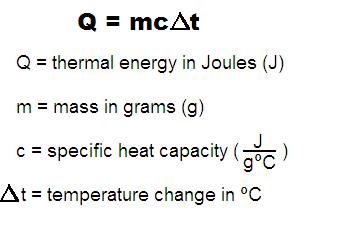
Examples
Simple
500g of water was heated from the initial temperature of 20°C to 50 °C. What is the change in thermal energy of water? (Heat capacity of water is 4.2J/g*°C)
1. Q = m*C*dT, Q=?, m=500g, C=4.2J/g*°C, dT=T_f-T_i
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Careful experiments show that the temperature increase of an object and its surroundings due to friction is directly related to the amount of mechanical energy lost. The most famous experimental demonstration of this fact was carried out by James Joule in the 1840’s. Joule hung some weights from pulleys so that as they fell, they turned a paddle-wheel apparatus immersed in a bucket of water. The friction between the paddles and the water raised the water’s temperature by an amount that was directly proportional to the distance that the weights fell. In our modern system of units, Joule found that raising the temperature of a kilogram of water by one degree Celsius required a loss in mechanical (gravitational) energy of approximately 4200 joules. Joule therefore proposed that this mechanical energy is not actually lost, but converted into a new type of energy: thermal energy, which manifests itself as an increase in temperature.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page
