Combining Electric and Magnetic Forces: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
When a charged particle is moving through a space with present electric and magnetic forces, if the forces are not balanced, the particles trajectory will change. It is important to remember that though the forces, observably, interact with a particle in different patterns, their effects can be quantitatively be compared. | When a charged particle is moving through a space with present electric and magnetic forces, if the forces are not balanced, the particles trajectory will change. It is important to remember that though the forces, observably, interact with a particle in different patterns, their effects can be quantitatively be compared. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 45: | ||
'''Quantitative:''' | '''Quantitative:''' | ||
'''Magnetic and Electric Forces together:''' | |||
The net force acting on a particle passing through a magnetic and electric field is: | |||
This formula is known as "Lorentz Force": | |||
''' | When the net force is equal to zero, the velocity stays constant. | ||
As seen in '''Figure 4''' , when the net forces acting on a particle are balanced the electric field, magnetic field, and velocity vector are all perpendicular to each other. The electric and magnetic forces are equal but opposite. | |||
Revision as of 13:28, 5 December 2015
Claimed by Alana Kaplan
When a charged particle is moving through a space with present electric and magnetic forces, if the forces are not balanced, the particles trajectory will change. It is important to remember that though the forces, observably, interact with a particle in different patterns, their effects can be quantitatively be compared.
Electric Forces:
Qualitative:
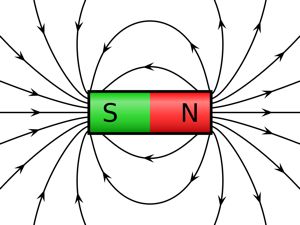
- • A particle being acted upon by an electric force will move in a straight line, in the path, or negative path depending on charge, of the the electric field line (See Figure 1) .
- • Electric fields point in a direction radially outward/ inward of a charged particle. There are four possible scenarios for the interaction of 2 charged particles:
- 1) A (-) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (-) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially outward from Particle(1)
- 2) A (+) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (-) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially inward toward Particle(1)
- 3) A (-) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (+) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially inward toward Particle(1)
- 4) A (+) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (+) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially outward from Particle(1)
- 1) A (-) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (-) charged particle(2)
Quantitative: The electric force formula is as follows:
Magnetic Forces:
- • The magnetic force on a charged particle is orthogonal to the magnetic field.
- • The particle must be moving with some velocity for a magnetic force to be present.
- • Particles move perpendicular to the magnetic field lines in a helical manner (See Figure 2)
- • To find the magnetic force, you can use the Right Hand Rule as follows (See Figure 3):
- 1) Thumb in direction of the velocity
- 2)Fingers in the direction of the magnetic field
- 3) Your palm will face in the direction of the Magnetic Force
Quantitative:
Magnetic and Electric Forces together:
The net force acting on a particle passing through a magnetic and electric field is:
This formula is known as "Lorentz Force":
When the net force is equal to zero, the velocity stays constant.
As seen in Figure 4 , when the net forces acting on a particle are balanced the electric field, magnetic field, and velocity vector are all perpendicular to each other. The electric and magnetic forces are equal but opposite.
