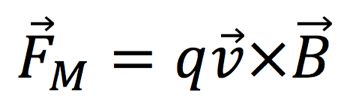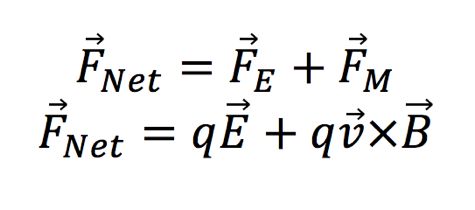Combining Electric and Magnetic Forces: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Claimed by Alana Kaplan | Claimed by Alana Kaplan | ||
PLEASE DO NOT EDIT THIS PAGE. COPY THIS TEMPLATE AND PASTE IT INTO A NEW PAGE FOR YOUR TOPIC. | PLEASE DO NOT EDIT THIS PAGE. COPY THIS TEMPLATE AND PASTE IT INTO A NEW PAGE FOR YOUR TOPIC. | ||
| Line 84: | Line 14: | ||
====Electric Forces==== | ====Electric Forces==== | ||
=====Qualitative===== | |||
[[File:ElectricForces.jpg|thumb| '''Figure 1.''' An electric force acts in a pattern parallel to the electric field, pointing radially inward or outward of a particle. The direction depends on the signs of the interacting charged particles. ]] | [[File:ElectricForces.jpg|thumb| '''Figure 1.''' An electric force acts in a pattern parallel to the electric field, pointing radially inward or outward of a particle. The direction depends on the signs of the interacting charged particles. ]] | ||
| Line 100: | Line 30: | ||
:::• Particle(2) feels force pointing radially outward from Particle(1) | :::• Particle(2) feels force pointing radially outward from Particle(1) | ||
=====Quantitative===== | |||
The electric force formula is as follows: | The electric force formula is as follows: | ||
| Line 140: | Line 71: | ||
The Lorentz Force calculation is one that is used now in many different applications. | The Lorentz Force calculation is one that is used now in many different applications. | ||
[[File:Velocityselector2.png|thumb| '''Figure 5.''' Illustration of a Velocity Selector ]] | [[File:Velocityselector2.png|thumb| '''Figure 5.''' Illustration of a Velocity Selector ]] | ||
| Line 152: | Line 83: | ||
===Simple=== | ===Simple=== | ||
Q: A proton is moving with velocity 7e8 in the +x direction. The trajectory of the proton is constant. There is an electric field in the area of 3.6e7 in the +y direction. Calculate the direction and magnitude of the present magnetic field? | |||
A: | |||
===Middling=== | ===Middling=== | ||
===Difficult=== | ===Difficult=== | ||
==Connectedness== | ==Connectedness== | ||
The Lorentz Force principle has been a component in many modern day inventions and critical building block for many physics principles. With known forces, we can calculate the very important figure, the speed of a moving particle. | |||
===Application: Velocity Selector=== | |||
[[File:Velocityselector2.png|thumb| '''Figure 5.''' Illustration of a Velocity Selector ]] | |||
The Velocity Selector is a device used to filter particles based on their velocity. A Velocity Selector uses controlled, perpendicular, electric and magnetic fields to filter certain charged particles (See '''Figure 5''' ). Particles with the correct speed will be unaffected while other particles will be deflected. This technique is used in technologies such as electron microscopes and spectrometers. | |||
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible | |||
===Other related topics=== | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 14:56, 5 December 2015
Claimed by Alana Kaplan
PLEASE DO NOT EDIT THIS PAGE. COPY THIS TEMPLATE AND PASTE IT INTO A NEW PAGE FOR YOUR TOPIC.
Short Description of Topic
The Main Idea
When a charged particle is moving through a space with present electric and magnetic forces, if the forces are not balanced, the particles trajectory will change. It is important to remember that though the forces, observably, interact with a particle in different patterns, their effects can be quantitatively be compared.
A Mathematical Model
Electric Forces
Qualitative
- • A particle being acted upon by an electric force will move in a straight line, in the path, or negative path depending on charge, of the the electric field line (See Figure 1) .
- • Electric fields point in a direction radially outward/ inward of a charged particle. There are four possible scenarios for the interaction of 2 charged particles:
- 1) A (-) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (-) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially outward from Particle(1)
- 2) A (+) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (-) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially inward toward Particle(1)
- 3) A (-) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (+) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially inward toward Particle(1)
- 4) A (+) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (+) charged particle(2)
- • Particle(2) feels force pointing radially outward from Particle(1)
- 1) A (-) charged Particle(1) is acting on a (-) charged particle(2)
Quantitative
The electric force formula is as follows:
Magnetic Forces
Qualitative
- • The magnetic force on a charged particle is orthogonal to the magnetic field.
- • The particle must be moving with some velocity for a magnetic force to be present.
- • Particles move perpendicular to the magnetic field lines in a helical manner (See Figure 2)
- • To find the magnetic force, you can use the Right Hand Rule as follows (See Figure 3):
- 1) Thumb in direction of the velocity
- 2)Fingers in the direction of the magnetic field
- 3) Your palm will face in the direction of the Magnetic Force
Quantitative
The magnetic force on an object is:
Note that if the velocity and magnetic field are parallel the magnetic force is zero.
Electric and Magnetic Forces Combined
The net force acting on a particle passing through a magnetic and electric field is:
This net force calculation is known as "Lorentz Force"
When the net force is equal to zero, the velocity stays constant. The net force is equal when:
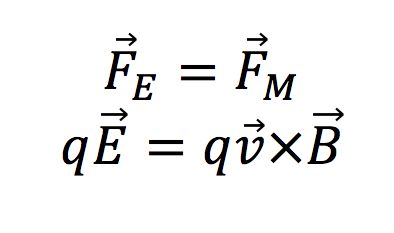
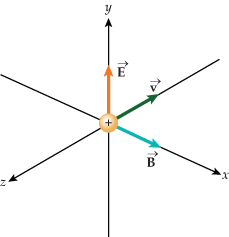
As seen in Figure 4 , when the net forces acting on a particle are balanced the electric field, magnetic field, and velocity vector are all perpendicular to each other. The electric and magnetic forces are equal but opposite. When forces are not balanced the trajectory of the the particle will change. The Lorentz Force calculation is one that is used now in many different applications.
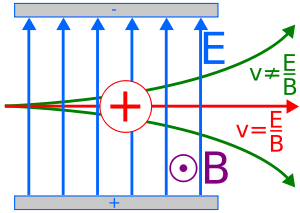
The Velocity Selector is a device used to filter particles based on their velocity. A Velocity Selector uses controlled, perpendicular, electric and magnetic fields to filter certain charged particles (See Figure 5 ). Particles with the correct speed will be unaffected while other particles will be deflected. This technique is used in technologies such as electron microscopes and spectrometers. Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Examples
Simple
Q: A proton is moving with velocity 7e8 in the +x direction. The trajectory of the proton is constant. There is an electric field in the area of 3.6e7 in the +y direction. Calculate the direction and magnitude of the present magnetic field?
A:
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
The Lorentz Force principle has been a component in many modern day inventions and critical building block for many physics principles. With known forces, we can calculate the very important figure, the speed of a moving particle.
Application: Velocity Selector

The Velocity Selector is a device used to filter particles based on their velocity. A Velocity Selector uses controlled, perpendicular, electric and magnetic fields to filter certain charged particles (See Figure 5 ). Particles with the correct speed will be unaffected while other particles will be deflected. This technique is used in technologies such as electron microscopes and spectrometers. Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page