Ohm's Law: Difference between revisions
Mtrussell6 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mtrussell6 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
===A Mathematical Model=== | ===A Mathematical Model=== | ||
While most often represented as <math>{I = \frac{|\Delta V|}{R}}</math>, Ohm's Law may also be represented as <math>V = IR</math> or <math>{R = \frac{V}{I}}</math>. Noteworthy is the fact that Ohm's Law depends upon Ohmic resistance and near ideal conductors to be accurate. Fortunately, most simple circuits without capacitance or inductance | While most often represented as <math>{I = \frac{|\Delta V|}{R}}</math>, Ohm's Law may also be represented as <math>V = IR</math> or <math>{R = \frac{V}{I}}</math>. Noteworthy is the fact that Ohm's Law depends upon Ohmic resistance and near ideal conductors to be accurate. Fortunately, most simple circuits without capacitance or inductance fit this criteria as the wires offer minuscule resistance when compared to the various resistors in the circuit. Additionally at any given point in time, Ohm's Law applies to both [http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/AC alternating current] and direct current. Also worth noting is that '''V''' does not necessarily represent the potential difference across a single source of electric potential (e.g. a battery) but rather the absolute value of the potential difference across an entire circuit. | ||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
There are numerous programs to be found that simulate circuits via Ohm's Law, with many allowing for analysis beyond the standard scope of Ohm's Law. One such example is [https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc Phet's Circuit Construction Kit], a free, lightweight tool to create and analyze simple DC current circuits. [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4ljzvLQG5tY Here] is a video briefly describing its installation and use! | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
Revision as of 16:56, 5 December 2015
WIP -- Claimed by Max Trussell
Ohm's law is very famous equation discovered by Georg Ohm describing the proportional relationship between voltage and current through some conductor. Most commonly this equation is seen in the form of
![]() , with I representing current in amperes, V representing electric potential in volts, and R the resistance in ohms.
, with I representing current in amperes, V representing electric potential in volts, and R the resistance in ohms.
The Main Idea
Stripped down to its most basic, Ohm's Law exists so that either the electric potential, current, or total resistance of some conductor may be found when two out of the three are known quantities. This is possible because of the simple, linear relationship between the three.
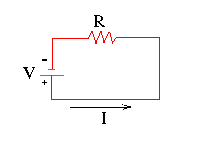
A Mathematical Model
While most often represented as [math]\displaystyle{ {I = \frac{|\Delta V|}{R}} }[/math], Ohm's Law may also be represented as [math]\displaystyle{ V = IR }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ {R = \frac{V}{I}} }[/math]. Noteworthy is the fact that Ohm's Law depends upon Ohmic resistance and near ideal conductors to be accurate. Fortunately, most simple circuits without capacitance or inductance fit this criteria as the wires offer minuscule resistance when compared to the various resistors in the circuit. Additionally at any given point in time, Ohm's Law applies to both alternating current and direct current. Also worth noting is that V does not necessarily represent the potential difference across a single source of electric potential (e.g. a battery) but rather the absolute value of the potential difference across an entire circuit.
A Computational Model
There are numerous programs to be found that simulate circuits via Ohm's Law, with many allowing for analysis beyond the standard scope of Ohm's Law. One such example is Phet's Circuit Construction Kit, a free, lightweight tool to create and analyze simple DC current circuits. Here is a video briefly describing its installation and use!
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page