Supersymmetry: Difference between revisions
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Hironari Miyazawa was the first person to propose supersymmetry, and his was relating mesons and baryons. Because of how broken his symmetry was, his work was largely ignored. 2 groups of scientists all independently began working on a supersymmetry in quantum field theory around the same time, J. L. Gervais and B. Sakita(1971), Yu. A. Golfand and E. P. Likhtman(1971), and D. V. Volkov and V. P. Akulov(1972). The Gervais-Sakita works arose because of an early version of string theory. The model proposed by Pierre Fayet known as the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model was the first realistic model in superstring theory proposed. | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 19:44, 5 December 2015
Short Description of Topic
The Main Idea
The main idea being discussed is the popular particle physics theory, Supersymmetry. One of the main goals of supersymmetry is to unify Quantum Theory with Einstein's General Relativity(Gravity). It does so by enumerating different types of elementary particles found in our universe to explain happenings in the microverse, by relating two types of elementary particles, Bosons and Fermions. Each particle from one group would have a super partner in the other group which has the a different weight, and the spin being separated by half an integer.
State, in your own words, the main idea for this topic
Consequences of Supersymmetry
One of the consequences of Supersymmetry would be that the number of particles that we know now in the standard model would be doubled. This is so that the super particles can counteract their regular particles much like anti-matter does for matter. Supersymmetry can also help to link the strong, weak, and electromagnetic forces together
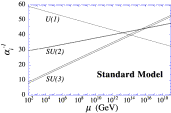
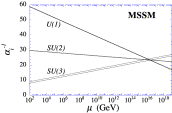
In the first graph above you can see that in the standard model without supersymmetry at high energies the three forces become close to each other. In the graph to the left of that however you can see that with supersymmetry the three become equal at some high energy point. Another interesting consequence that could come of supersymmetry is the explanation of what dark matter is. Normal matter, the things we can observe in our everyday lives, is approximately 4% of the known universe. Dark matter is thought to take up more than 20% of our known universe, and supersymmetry could help to explain that. Dark matter are weakly interacting particles that are thought to help bind large bodies together despite what would normally be weak gravitational pull between them at the speeds they move, such as galaxies. Galaxies move too quickly for the stars contained within them to stay bound without dark matter.
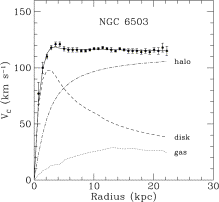
The graph above shows how fast the velocities within a solar system should be at size without dark matter, and then above all of these graphs is shown how fast they are actually moving.
A Mathematical Model
What are the mathematical equations that allow us to model this topic. For example [math]\displaystyle{ {\frac{d\vec{p}}{dt}}_{system} = \vec{F}_{net} }[/math] where p is the momentum of the system and F is the net force from the surroundings.
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Hironari Miyazawa was the first person to propose supersymmetry, and his was relating mesons and baryons. Because of how broken his symmetry was, his work was largely ignored. 2 groups of scientists all independently began working on a supersymmetry in quantum field theory around the same time, J. L. Gervais and B. Sakita(1971), Yu. A. Golfand and E. P. Likhtman(1971), and D. V. Volkov and V. P. Akulov(1972). The Gervais-Sakita works arose because of an early version of string theory. The model proposed by Pierre Fayet known as the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model was the first realistic model in superstring theory proposed.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page