Rutherford Experiment and Atomic Collisions: Difference between revisions
Mbaskaran3 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Vhariharan8 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Claimed by: | Claimed by: vhariharan8 (Spring 2017) | ||
==Atomic Collisions Modeled through the Gold Foil Experiment== | ==Atomic Collisions Modeled through the Gold Foil Experiment== | ||
Revision as of 23:16, 23 March 2017
Claimed by: vhariharan8 (Spring 2017)
Atomic Collisions Modeled through the Gold Foil Experiment
This topic discusses how Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment helped to demonstrate the physics behind atomic collisions. The alpha particles collided with the gold foil and as a result some experienced deflection and back scattering of some of the particles was observed. This was not originally hypothesized due to the idea that, at most the alpha particle should experience only a 90° scattering angle. This helped lead to the discovery of the nucleus and a highly compact positively charged center. It also validated two laws of conservation, that of momentum and that of energy. This showed that atomic collision act as inelastic collision.

History
There was little known information about atoms apart from the fact that they contained electrons as discovered by J.J. Thompson in 1897. Thompson helped to create the speculation that electrons were negatively charged particles. It was also speculated that there must be a positive charge to balance out the negative charge from the electron. At this time, the plum pudding model was also created by Thompson who stated that matter was made of atoms that were spheres of positive charge with electrons proliferated throughout. The electrons function as the plum that was evenly distributed through a positively charged pudding.
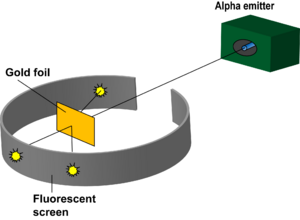
In 1911, Ernest Rutherford carried out an experiment to test the plum pudding model. He shot helium particles at gold foil in order to measure the deflection of the particles as they come off of the other side. He was able to deduce that a majority of the particles went straight through which helped to indicate that the atom is made predominantly of empty space with a small nucleus with protons and electrons placed extremely far away from the nucleus in their own cloud.
A Mathematical Model
Rutherford modeled the effect the alpha particle has on the electrons of the gold atom. He did this by calculating the potential electric energy between the particle and the atom using the formula below.
[math]\displaystyle{ {U_{elec}} = {\frac{1}{4πε_0}}{\frac{q_{α}q_{Au}}{r}} }[/math]
Where:
r = center to center distance between particle and atom
[math]\displaystyle{ {\frac{1}{4πε_0}} = {9*10^9}{\frac {N*m^2}{C^2}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {q_α} }[/math] = charge of alpha particle
[math]\displaystyle{ {q_{Au}} }[/math] = charge of gold nucleus
In this instance the charge of the alpha particle is equal to 2e and the charge of the gold particle is equal to 79e.
Another important part of atomic collisions is that they are inelastic collisions. This is shown by the conservation of both momentum and kinetic energy. Take the alpha particle and gold particle for example.
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{α,i}}} = {\vec{p_{α,f}}}+ {\vec{p_{Au,f}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{K_{α,i}}} = {\vec{K_{α,f}}}+ {\vec{K_{Au,f}}} }[/math]
Where [math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p}} }[/math] is momentum and [math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{K}} }[/math] is kinetic energy.
A Computational Model
Much like the mathematical model, the collision can be modeled computationally using the same formulas. In order to view this better, here is a Rutherford Scattering Model.
Example Problems
Example 1
Two protons start far apart. One has an initial momentum of [math]\displaystyle{ {\lt 5.1*10^{-4},0,0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}} }[/math] and it approaches the other proton, at rest. The two protons repel each other and one now has a momentum of [math]\displaystyle{ {\lt 3.5*10^{-4},2.7*10^{-4},0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}} }[/math]. What is the new momentum of the other proton?
Solution
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{1,i}}}= {\lt 5.1*10^{-4},0,0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{2,i}}}= {\lt 0,0,0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{1,f}}}= {\lt 3.5*10^{-4},2.7*10^{-4},0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{2,f}}}= {?} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{tot,i}}}={\vec{p_{tot,f}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\lt 5.1*10^{-4},0,0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}+\lt 0,0,0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}}={\lt 3.5*10^{-4},2.7*10^{-4},0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}+{\vec{p_{2,f}}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\lt 5.1*10^{-4},0,0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}-\lt 3.5*10^{-4},2.7*10^{-4},0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}}={\vec{p_{2,f}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {\vec{p_{2,f}}}={\lt 1.6*10^{-4},-2.7*10^{-4},0\gt }{kg*{\frac{m}{s}}} }[/math]
Example 2
A proton and an electron are a distance [math]\displaystyle{ {7.2*10^{-9}m} }[/math] apart. What is the electric potential energy of the system consisting of the proton and the electron?
Solution
[math]\displaystyle{ {U_{elec}} = {\frac{1}{4πε_0}}{\frac{q_{+}q_{-}}{r}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {U_{elec}} = {9*10^{9}}{\frac {N*m^2}{C^2}}*{\frac{1.6*10^{-19}*(-1.6*10^{-19})}{7.2*10^{-9}}} = {-3.2*10^{-28}}{J} }[/math]
Connectedness
This topic is related to the study of biochemistry because without the discovery of the nucleus any progress in this field would be limited based on the interaction of atomic particles. This would also hinder the field medicine for very similar reason. Much of the understanding of sciences has its roots in the understanding of the atom and its functions. This experiment and the idea of atomic collisions helped to widen the atomic grasp. One of the best industrial examples of the is the Large Hadron Collider.
History
With the knowledge of the plum pudding model of the atom, Ernst Rutherford and a small group of scientists set out to discover the properties behind alpha particles. The experiment, now known as the Gold Foil Experiment, was used to test this in 1911. It involved launching alpha particles at a small piece of gold foil. It was hypothesized that the alpha particle would be deflected at times, but at an angle because it was assumed that the alpha particle was more dense than the gold foil atom. They registered deflected particles through light emissions that would occur when the alpha particle hit the light source. Much to their surprise, some of the alpha particles they launched bounced straight back. This demonstrated that the gold particle was more massive than expected. It led to the discovery that the atom contained a positively charged nucleus. This was a major break through in the study of the atom in that it showed what the atoms composition was and how it act around other atoms.
References
"History of Rutherford Experiment". HyperPhysics. Web. 03 Dec. 2015. Retrieved from: <http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hframe.html>.
Chabay, R.W., & Sherwood, B.A. (2015). Collisions. In Fiorillo, J. Editor & Rentrop, A. Editor (Eds.), Matter and Interactions (383-410). John Wiley & Sons, Inc.