Light Propagation Through a Medium: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==The Main Idea== | ==The Main Idea== | ||
When light travels through anything but a vacuum the speed of light travels at a speed different from c=3.00E8 and the light particles scatter. The highest speed that light can travel though is the universal constant c. | When light travels through anything but a vacuum the speed of light travels at a speed different from c=3.00E8 m/s and the light particles scatter. The highest speed that light can travel though is the universal constant c. | ||
===A Mathematical Model=== | ===A Mathematical Model=== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
[[File:snell-anim.gif]] | [[File:snell-anim.gif]] | ||
==Examples== | |||
===Easy=== | |||
The speed of light is measured to be 2.76E8 m/s, What is the index of refraction for the medium. | |||
===Medium=== | |||
===Difficult=== | |||
==Connectedness== | |||
==History== | |||
==See Also== | |||
Revision as of 22:40, 23 November 2017
This page is going to be about about Light Propagation. A work in progress . Edited by Roshan Konda Fall 2017
The Main Idea
When light travels through anything but a vacuum the speed of light travels at a speed different from c=3.00E8 m/s and the light particles scatter. The highest speed that light can travel though is the universal constant c.
A Mathematical Model
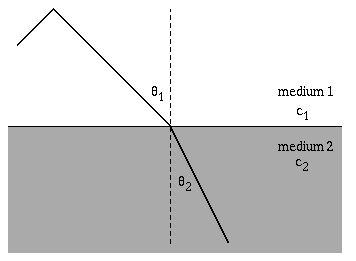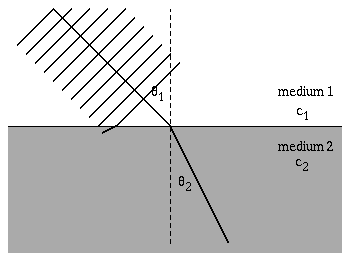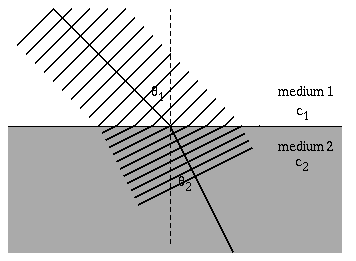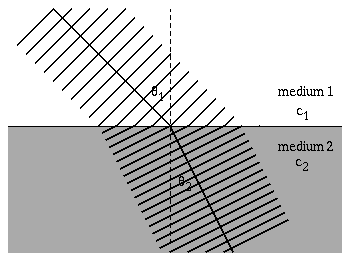
The speed of light through a medium can be given by the formula n=(c/v), where n is the index of refraction, v is the velocity of light through the medium and c is the speed of light through a vacuum.
A Computational Model
Examples
Easy
The speed of light is measured to be 2.76E8 m/s, What is the index of refraction for the medium.