Curly Electric Fields: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
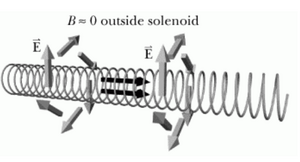
However, in the situation where current in the solenoid is changing and magnetic force is thereby time-varying, a '''curly electric field''' can be observed. | However, in the situation where current in the solenoid is changing and magnetic force is thereby time-varying, a '''curly electric field''' can be observed. | ||
[[File:curlyefield2.png| | [[File:curlyefield2.png|300px|thumb|left|''The '''curly electric field''' is a result of changing current and time-varying magnetic field'']] | ||
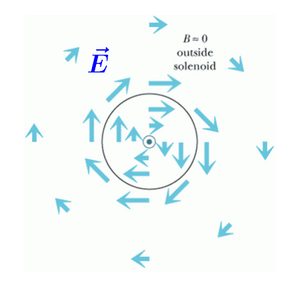
[[File:curlyefield1.png| | [[File:curlyefield1.png|300px|thumb|right|''Outside of the solenoid, magnetic field is still virtually zero, but the curly electric field can be observed both inside and outside of the solenoid'']] | ||
Revision as of 17:08, 1 December 2015
This topic is claimed by Miranda Fyfe.
Curly Electric Fields
In the case where current in a solenoid is constant and magnetic force is likewise constant in time, it can be observed that the magnetic and electric forces experienced by some moving charge outside the solenoid are essentially zero.
However, in the situation where current in the solenoid is changing and magnetic force is thereby time-varying, a curly electric field can be observed.