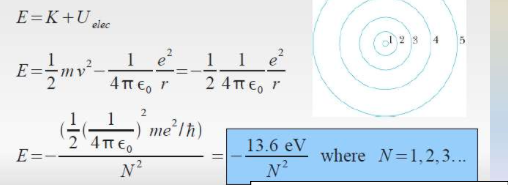Bohr Model: Difference between revisions
Pearlruparel (talk | contribs) |
Pearlruparel (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[File:Screen Shot 2015-12-01 at 6.15.49 PM.png]] As discovered by Neil | [[File:Screen Shot 2015-12-01 at 6.15.49 PM.png]] As discovered by Neil Bohr, the radius can be derived from using the angular momentum equation. The electron in only allowed to live in certain levels. Thus the radius is calculated. | ||
Bohr, the radius can be derived from using the angular momentum equation. | |||
[[File:Screen_Shot_2015-12-01_at_6.17.32_PM.png]] | [[File:Screen_Shot_2015-12-01_at_6.17.32_PM.png]] | ||
The total energy is also calculated through using this model. | |||
[[File:Screen Shot 2015-12-01 at 6.26.02 PM.png]] | |||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 1 December 2015
by Pearl Ruparel
Main Idea
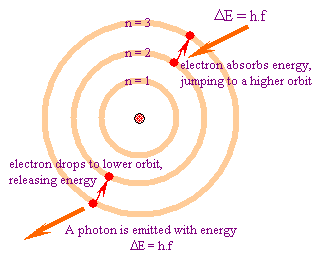
In atomic physics, the Bohr model depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons in orbit similar in structure to the solar system. In the Bohr Model the neutrons and protons occupy a dense central region (the nucleus), while the electrons orbit the nucleus, like the planets orbit the Sun. That is why the Bohr Model is commonly referred tot as the "planetary model".It is taught as an introduction to quantum physics. In the Bohr Model, electrons can only be at certain, discrete, distances from the proton to which it is bound. Energy is quantized as explained by the Bohr Model. This means that only orbits with certain radii are allowed, while orbits in between simply don't exist. These levels are knows an quantized energy levels and are labeled with integer N known as quantum number. The lowest energy state is generally termed the ground state. The states with successively more energy than the ground state are called the first excited state, the second excited state, and so on. As the electrons become further away from the nucleus, they become larger and have higher energy. Beyond an energy called the ionization potential the single electron of the hydrogen atom is no longer bound to the atom. The Bohr model works well for very simple atoms such as hydrogen (which has 1 electron) but not for more complex atoms. Although the Bohr model is still used today, especially in elementary textbooks, a more sophisticated (and complex) model — the quantum mechanical model — is used much more frequently.
A Mathematical Model
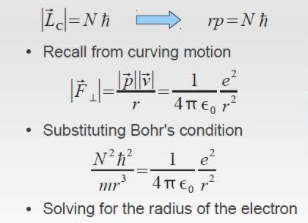 As discovered by Neil Bohr, the radius can be derived from using the angular momentum equation. The electron in only allowed to live in certain levels. Thus the radius is calculated.
As discovered by Neil Bohr, the radius can be derived from using the angular momentum equation. The electron in only allowed to live in certain levels. Thus the radius is calculated.
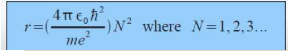
The total energy is also calculated through using this model.
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
The first successful model of hydrogen was developed by Bohr in 1913, and incorporated the new ideas of quantum theory. Neil Bohr explained the emission spectra of hydrogen by improving on the Rutherford model of the atom. Initially, Rutherford's planetary model predicted a continuous spectrum of light from hydrogen. However, Bohr corrected for this by proposing that the translational angular momentum of the electron can be quantized. Although this model is not entirely correct, it has many features that are and is therefore used in physics.
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page