Temperature: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Measurement=== | ===Measurement=== | ||
[[File: | [[File:Thermometer11.jpg|200px|thumb|right(position)|]] | ||
A thermometer is a device used to measure temperature. It is placed in contact with an object and allowed to reach thermal equilibrium with the object. The operation of a thermometer is based on some property, such as volume, that varies with temperature. For example, mercury in a mercury thermometer expands to a degree depending on a temperature of the object and the level of the mercury in side the glass tube rises or descends. | A thermometer is a device used to measure temperature. It is placed in contact with an object and allowed to reach thermal equilibrium with the object. The operation of a thermometer is based on some property, such as volume, that varies with temperature. For example, mercury in a mercury thermometer expands to a degree depending on a temperature of the object and the level of the mercury in side the glass tube rises or descends. | ||
Temperature can be measured in numbers by three temperature scales: Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Celsius scale sets freezing point of the water at zero and boiling point at 100, and Fahrenheit scale sets freezing point of the water at 32 degrees and boiling point of the water at 212 degrees. Kelvin scale is designed to go to zero at absolute zero, the minimum temperature. | Temperature can be measured in numbers by three temperature scales: Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Celsius scale sets freezing point of the water at zero and boiling point at 100, and Fahrenheit scale sets freezing point of the water at 32 degrees and boiling point of the water at 212 degrees. Kelvin scale is designed to go to zero at absolute zero, the minimum temperature. | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 5 December 2015
Defining temperature
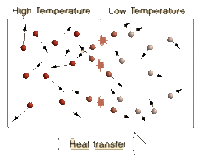
Temperature is measure of average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. Difference between temperature and heat is that heat is the sum of all the kinetic energies of the particles in a system. Adding heat to a system causes its temperature to rise. Newton's zeroth law states that a system reaches a thermal equilibrium when there is no observable change in temperature between a system. Therefore, the change in temperature causes heat to flow from a high temperature system to a low temperature system. When systems with different temperature is in contact, molecules with higher kinetic energy collide with molecules with lower kinetic energy, kinetic energy is passed from the molecules with more kinetic energy to those with less kinetic energy. This molecular level of kinetic energy transfer will happen until average kinetic energy of the particles in each systems reach the average of two.
The relationship between heat transfer and temperature can be modeled with this equation: Q = m c Delta T
Measurement
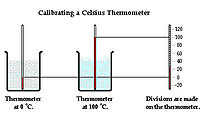
A thermometer is a device used to measure temperature. It is placed in contact with an object and allowed to reach thermal equilibrium with the object. The operation of a thermometer is based on some property, such as volume, that varies with temperature. For example, mercury in a mercury thermometer expands to a degree depending on a temperature of the object and the level of the mercury in side the glass tube rises or descends. Temperature can be measured in numbers by three temperature scales: Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Celsius scale sets freezing point of the water at zero and boiling point at 100, and Fahrenheit scale sets freezing point of the water at 32 degrees and boiling point of the water at 212 degrees. Kelvin scale is designed to go to zero at absolute zero, the minimum temperature.
The relationship between temperature scales: (degrees)K = 273.15 + (degrees)C (degrees)C = (5/9)*((degrees)F-32) (degrees)F = (9/5)*(degrees)C+32
Thermal Expansion
Change in temperature through heat transfer can change the matter to change in shape, area, and volume. When a substance is heated, the kinetic energy of its molecules increases. Then the molecules begin moving more and average separation between molecules become larger, and thus volume of the substance changes. The degree of expansion divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature and the object and state of matter of the object.
| Material | Fractional expansion per degree C x10^-6 | Fractional expansion per degree F x10^-6 |
|---|---|---|
| Glass, ordinary | 9 | 5 |
| Glass, pyrex | 4 | 2.2 |
| Quartz, fused | .59 | .33 |
| Aluminum | 24 | 13 |
| Brass | 19 | 11 |
| Copper | 17 | 9.4 |
| Iron | 12 | 6.7 |
| Steel | 13 | 7.2 |
| Platinum | 9 | 5 |
| Tungsten | 4.3 | 2.4 |
| Gold | 14 | 7.8 |
| Silver | 18 | 10 |
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/tables/thexp.html
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/temper.html