Kinds of Matter: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==Connectedness== | ==Connectedness== | ||
The different kinds of matter are important to understanding how physics can be applied to everyday life. It helps connect the misunderstood atomic and subatomic level to something that everyone can understand. More advanced physics will correlate atomic bonds to springs, a juxtaposition that helps explain a complex interaction with a simple explanation. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
[[Detecting Interactions]] | [[Detecting Interactions]] | ||
[[Atoms]] | |||
[[Solids]] | |||
[[Liquids]] | |||
[[Gas]] | |||
===External links=== | ===External links=== | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 5 December 2015
Claimed by Kristen Sparks
This topic covers the Different Kinds of Matter.
The Main Idea
No matter how how big or small the matter, physics can be applied to all objects.
Atoms and Nuclei
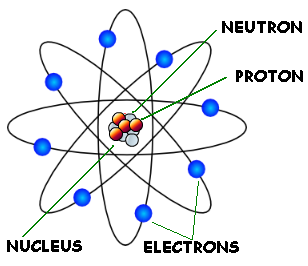
All matter is made of atoms. To understand the properties of matter around us we look at atomic properties and interactions. Atomic interactions can be attributed to the attractive and repulsive forces due to the different parts of an atom which are: protons, electrons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons make up a small, dense center called a nucleus. Around the nucleus are electrons, whose negative forces are attracted to the positive center.
The number of neutrons and protons in specific chemical elements can be found on the periodic table.
Molecules and Solids
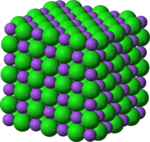
When atoms bond together molecules are formed. Molecules can be made up of any number of chemical elements, but as a whole the molecule's properties differ from the properties of its subelements.
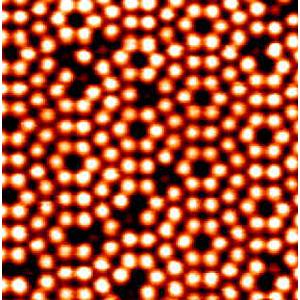
Solids are rigid objects made up of molecules. Scanning tunneling microscopes (STMs) are used to see molecules and atoms that make up everyday solids. STMs can observe patterns and irregularities that may occur on the surface of solids, which have helped scientists understand more about what happens on the atomic level of matter.
Liquids and Gases
Liquids are formed when solids are heated. Atoms begin to vibrate too fast to maintain their normal rigid positions. If the temperature increases enough atoms will start to shift past one another therefore becoming a liquid. If the temperature is further increased the sliding of atoms will turn into interatomic bond breaking which will lead to gas formation.
Planets, Stars, Solar Systems and Galaxies
Plants and stars make up solar systems, and multiple solar systems make up galaxies.
Point Particles
Point particles are often used to analyze more complicated/large objects. Physicists assume that these objects have been compressed into structures where size, shape and internal structure are not taken into consideration: a tiny speck with equivalent mass as the object its representing.
Examples
Atom
Crystalline Solid
STM Image
Connectedness
The different kinds of matter are important to understanding how physics can be applied to everyday life. It helps connect the misunderstood atomic and subatomic level to something that everyone can understand. More advanced physics will correlate atomic bonds to springs, a juxtaposition that helps explain a complex interaction with a simple explanation.
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Detecting Interactions Atoms Solids Liquids Gas
External links
http://www.livescience.com/46506-states-of-matter.html
References
Matter and Interactions By Ruth W. Chabay, Bruce A. Sherwood - Chapter 1