Projectile Motion: Difference between revisions
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
===External links=== | ===External links=== | ||
[http://www. | [http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Vectors-and-Projectiles/Projectile-Simulator Interactive Projectile Simulator] | ||
[http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Vectors-and-Projectiles/Projectile-Simulator/Projectile-Simulator-Exercise-1 Projectile Simulator] | |||
[http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Vectors-and-Projectiles/Projectile-Simulator/Projectile-Simulator-Exercise-2 Horizontally-Launched Projectiles] | |||
[http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Vectors-and-Projectiles/Projectile-Simulator/Projectile-Simulator-Exercise-3 Angle-Launched Projectiles] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 6 December 2015
claimed by ngillis3
This page will attempt to analyze projectile motion, a branch of classical mechanics in which the motion of an object (the projectile) is analyzed under the influence of the constant acceleration of gravity, after it has been propelled with some initial velocity.
The Main Idea
Let us imagine firing a cannon, or throwing the ball off of a tower, driving a golf ball off of a tee or even shooting a basketball. All of these are examples of projectile motion. By definition, a projectile has a single force that acts upon it - the force of gravity. If there were any other force acting upon an object, then that object would not be a projectile. Thus projectile motion is motion under the primary action of gravity where the initial velocity in some horizontal direction is not zero.
A Mathematical Model
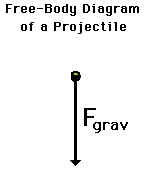
Regardless of whether a projectile is moving upwards, downwards, upwards and rightwards, or downwards and leftwards, the free-body diagram of the projectile is still modeled as an object upon which the only force is gravity. Thus, the free-body diagram of a projectile would show a single force acting downwards and labeled force of gravity (or simply Fgrav).
[math]\displaystyle{ \vec{F}_{grav} = mg\hat{y} }[/math]
where m is the mass of the projectile and
g represents the acceleration due to Earth's gravitational field.
A Computational Model
One method used to visualize or predict a projectiles trajectory is to apply our mathematical model using computational programming. Please see the following Projectile Motion Video for a detailed computational model including animation of a projectile in motion. For this computational model I used V-Python!
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
Projectile motion represents my most cherished triumph in developing my skills in physics analysis. I chose the topic of Projectile Motion because it was my primary introduction to Kinetics and Kinematics. For me, the study of projectile motion was a relevant and practical analysis that allowed me to analyze something that I could visualize and tangibly model. If ever there was a problem that I didn't understand, it was easy to represent the projectile in my own model and derive a reasonable approximation or solution. Analysis of projectile motion made me confident in my own physics intuition! After all my first physics teacher used to always say, "If gravity is about 10, does your answer make sense?"
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Interactive Projectile Simulator Projectile Simulator Horizontally-Launched Projectiles Angle-Launched Projectiles
References
The following references were used while writing this page:
https://www.phy.duke.edu/~rgb/Class/intro_physics_1/intro_physics_1.pdf http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/Lesson-2/What-is-a-Projectile