Inclined Plane: Difference between revisions
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
:<math>\F_w\</math> is a gravitational force that applies on the plane<br> | :<math>\F_w\</math> is a gravitational force that applies on the plane<br> | ||
F_i is a force exerted on the object and parallel to the plane<br> | F_i is a force exerted on the object and parallel to the plane<br> | ||
:<math>\mathrm{MA} = \ | :<math>\mathrm{MA} = \{F_w}{F_i}. \,</math><br> | ||
Revision as of 23:58, 26 November 2016
Definition
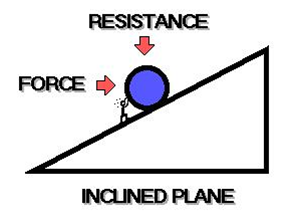
inclined(adj): deviating in direction from the horizontal or vertical; sloping
plane(n):a flat or level surface
Inclined plane means a plane with a level surface. It is inclined at a angle to the horizontal.
Uses
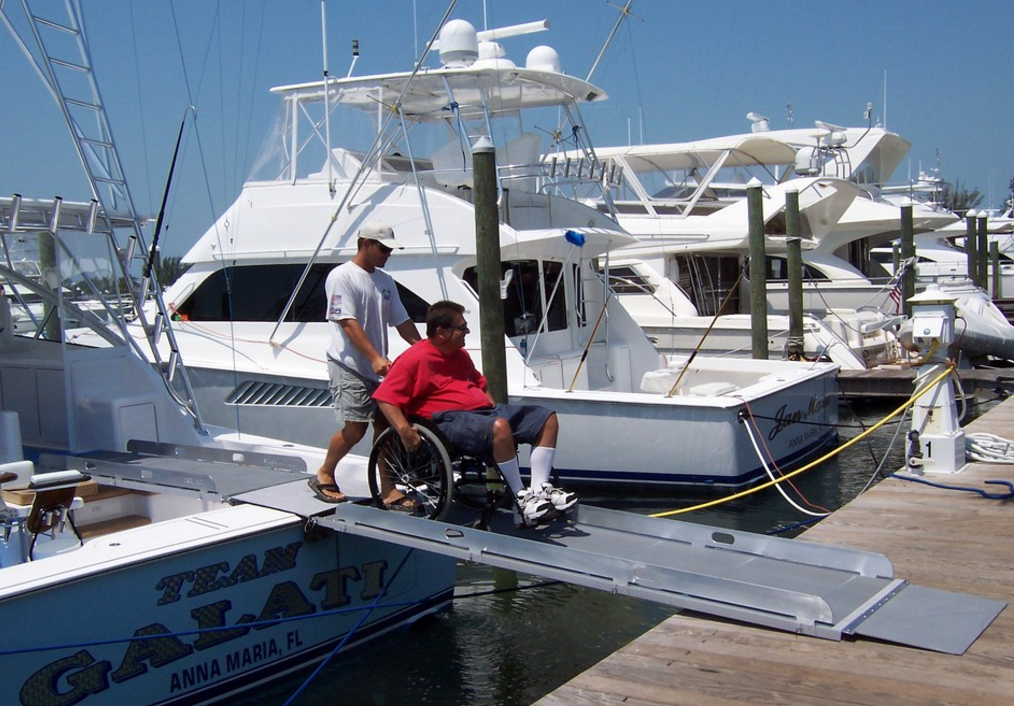
You may see this almost every day in your daily life. The inclined planes are needed for loading and unloading heavy goods on transportation such as ships, trucks and planes because it has mechanical advantage of reducing the forces required to move heavy goods.
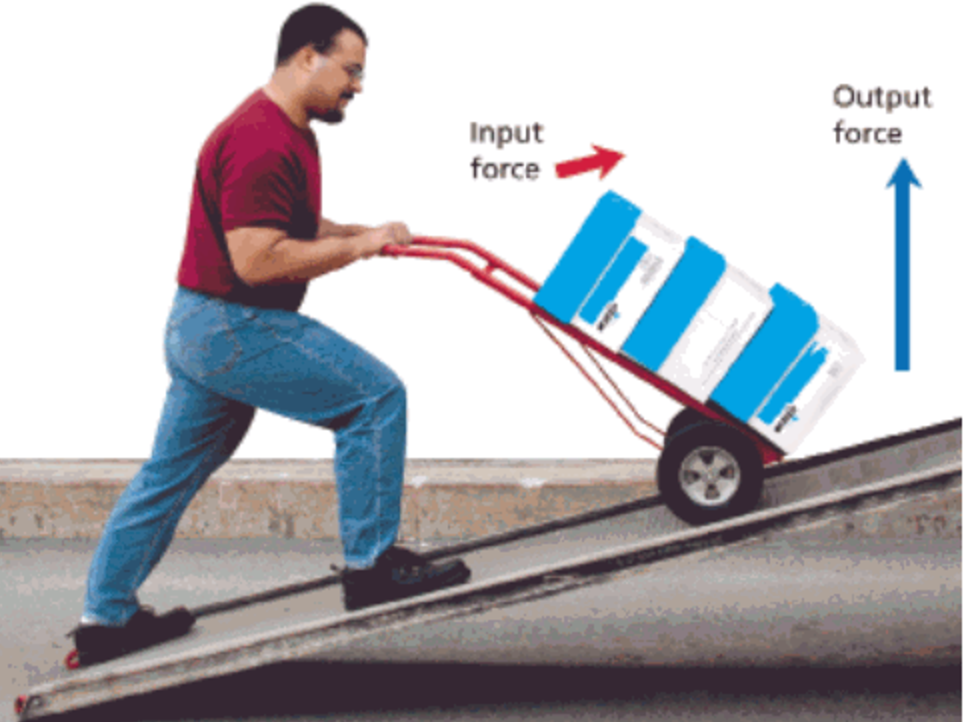


Physics of the Inclined Plane
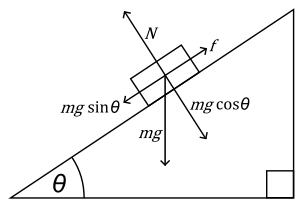
θ= Angle of the plane to the horizontal
g= Acceleration due to gravity
m= Mass of object
N= Normal force (perpendicular to the plane)
f = frictional force of the inclined plane (sometimes it is omitted on test problems)
mgSinθ= A force parallel to the plane (mgSinθ > f the body slides down the plane)
mgCosθ= A force acting into the plane (opposite to N)
Mechanical Advantage
- [math]\displaystyle{ \F_w\ }[/math] is a gravitational force that applies on the plane
F_i is a force exerted on the object and parallel to the plane
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{MA} = \{F_w}{F_i}. \, }[/math]