Meissner effect: Difference between revisions
Austincale96 (talk | contribs) |
Austincale96 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
It was mentioned that when a superconductor is exposed to a magnetic field greater than the critical magnetic field, it breaks down. Through experimentation, the critical temperature can be found, as well as the critical magnetic field at 0 kelvin. After these two values are known, the relationship between critical magnetic field and temperature can be found in the following equation. | It was mentioned that when a superconductor is exposed to a magnetic field greater than the critical magnetic field, it breaks down. Through experimentation, the critical temperature can be found, as well as the critical magnetic field at 0 kelvin. After these two values are known, the relationship between critical magnetic field and temperature can be found in the following equation. | ||
:<math> B_c \approx | :<math> B_c \approx B_(c0) [1 - \left ( \frac{T}{T_c} \right ) ^2] | ||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
Revision as of 22:34, 27 November 2016
CLAIMED BY AUSTIN CALE (austincale96) [FALL 2016]
What is the Meissner Effect
The Meissner effect is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state. Below the transition temperature, superconductors cancel nearly all interior magnetic fields actively. The effect that occurs, leading to a zero net magnetic effect in the material, can be attributed to diamagnetism.
What is diamagnetism?
Some materials tend to expel a magnetic field, materials that do this are called diamagnetic, but the effects of this diamagnetism are weak. For example, water and the human body are diamagnetic materials. Diamagnetism is a weak repulsion from a magnetic field. It is a form of magnetism that is only exhibited by a substance in the presence of an externally applied magnetic field. It results from changes in the orbital motion of electrons. Applying a magnetic field creates a magnetic force on a moving electron in the form of F = Qv × B. This force changes the centripetal force on the electron, causing it to either speed up or slow down in its orbital motion. This changed electron speed modifies the magnetic moment of the orbital in a direction opposing the external field.
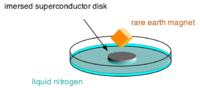
In superconducting material the Meissner effect creates currents which completely oppose the magnetic field applied by a magnet. In other words, they will repel a magnet, causing it to levitate. This consequently makes a superconductor in the Meissner state a perfect diamagnet.
How does it Work?
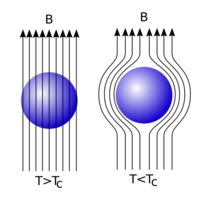
A superconductor with little or no magnetic field within it is said to be in the Meissner state and breaks down when the magnetic field is larger than the critical magnetic field.
A superconductor is fundamentally different from a conductor, because Faraday’s law of induction alone does not explain magnetic repulsion by a superconductor. At a temperature below its Critical Temperature, Tc, a superconductor will not allow any magnetic field to freely enter it. This is because microscopic magnetic dipoles are induced in the superconductor that oppose the applied field. This induced field then repels the source of the applied field, and will consequently repel the magnet associated with that field.
This implies that if a magnet was placed on top of the superconductor when the superconductor was above its Critical Temperature, and then it was cooled down to below Tc, the superconductor would then exclude the magnetic field of the magnet. This means that a magnet already levitating above a superconductor does not demonstrate the Meissner effect, while a magnet that is initially stationary and then repelled by a superconductor as it is cooled through its critical temperature does.
Type I and Type II Superconductors
There are two categories of superconductors that relate to the Meissner effect: Type I and Type II. Type I superconductors consist of pure metals that act as superconductors, while Type II superconductors are alloys that act as superconductors. Type I superconductors exclude magnetic fields completely due to the Meissner effect. Type II superconductors, on the other hand, are typically a mixture of normal and superconducting regions. This mixture causes Type II superconductors to not completely exclude magnetic fields, and instead constrain the fields to filaments within the material, creating what is sometimes referred to as the vortex state.
A Mathematical Model
It was mentioned that when a superconductor is exposed to a magnetic field greater than the critical magnetic field, it breaks down. Through experimentation, the critical temperature can be found, as well as the critical magnetic field at 0 kelvin. After these two values are known, the relationship between critical magnetic field and temperature can be found in the following equation.
- <math> B_c \approx B_(c0) [1 - \left ( \frac{T}{T_c} \right ) ^2]
A Computational Model
Examples
Simple
Medium
Difficult
What did it lead to?
The theory of the Meissner effect led to the phenomenological theory of superconductivity by Frits London and Heinz London in 1935. This theory explained resistance less transport and the Meissner effect, and allowed the first theoretical predictions for superconductivity to be made as seen below.
By using the London equations and Maxwell equations, one can predict how the magnetic field and surface current vary with distance from the surface of a superconductor.
Connectedness
The Meissner effect causes superconductors to exclude magnetic fields. Because of this exclusion, superconductors will repel magnets. Assuming the magnet is small enough that the repulsion can overcome the force of gravity, the magnet can be capable of levitating. This magnetic levitation has numerous applications, one of the most well-known being maglev trains. Maglev trains are convenient for many reasons; however, one of the most important advantages of maglev systems is the lack of friction between the train and the rails. This lack of friction creates benefits such as faster and quieter transportation, and also less maintenance required, because less friction means parts will last longer.
Further reading
Albert Einstein (1922). "Theoretical remark on the superconductivity of metals". arXiv:physics/0510251v2. Bibcode:2005physics..10251E. Fritz Wolfgang London (1950). "Macroscopic Theory of Superconductivity". Superfluids. Structure of matter series 1. OCLC 257588418.. Revised 2nd edition, Dover (1960) ISBN 978-0-486-60044-4. By the man who explained the Meissner effect. pp. 34–37 gives a technical discussion of the Meissner effect for a superconducting sphere.
External links
Videos to aid in the understanding of the concept.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=44mVZdnR6Yc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bnyB-PInFA4
References
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/solids/meis.html http://www.supraconductivite.fr/en/index.php?p=supra-levitation-meissner-more http://lrrpublic.cli.det.nsw.edu.au/lrrSecure/Sites/Web/physics_explorer/physics/lo/superc_12/superc_12_02.htm http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/webprojects2006/Truscott/paged_r.html http://www.imagesco.com/articles/superconductors/superconductor-meissner-efsfect.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Solids/maglev.html https://www.britannica.com/technology/maglev-train http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Solids/scond.html
See link to the right to read more on superconductors. [[1]]