Power in a circuit: Difference between revisions
Fishergreen (talk | contribs) |
Fishergreen (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
This topic is extremely important in examining infrastructure related to energy distribution. For example, in power grids, power lines are resistors, and therefore dissipate a certain amount of power. Since resistance is also related to the length of a wire, we can deduce that more power will be dissipated across longer power lines. | This topic is extremely important in examining infrastructure related to energy distribution. For example, in power grids, power lines are resistors, and therefore dissipate a certain amount of power. Since resistance is also related to the length of a wire, we can deduce that more power will be dissipated across longer power lines. | ||
Additionally, it is extremely important to understand the concept of power dissipated by a resistor in the field of Electrical Engineering. For example, knowing how to calculate power allows for the calculation of how large a resistor needs to be in order handle the energy dissipated through heat. | Additionally, it is extremely important to understand the concept of power dissipated by a resistor in the field of Electrical Engineering. For example, knowing how to calculate the power dissipated allows for the calculation of how large a resistor needs to be in order handle the energy dissipated through heat. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 17:03, 30 November 2015
Claimed by Hunter Brown Short Description of Topic
The Main Idea
Measuring the power in a circuit can provide useful insight into the ability of a circuit to accomplish a given task. In order to understand how to calculate and interpret power in a simple circuit, one must know the mechanical definition and significance of Power. For this section, we will be using the unit of Watt for power.
It is important to note that the power in parts of a circuit can be represented in several different ways. Most commonly, power in a circuit is expressed in terms of Voltage (E, Emf, Volts), Current (I, Amps), and Resistance (R, Ohms).
A Mathematical Model
The power dissipated in a resistor is [math]\displaystyle{ P=IV }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ P=I^2R }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ P=V^2/R }[/math]
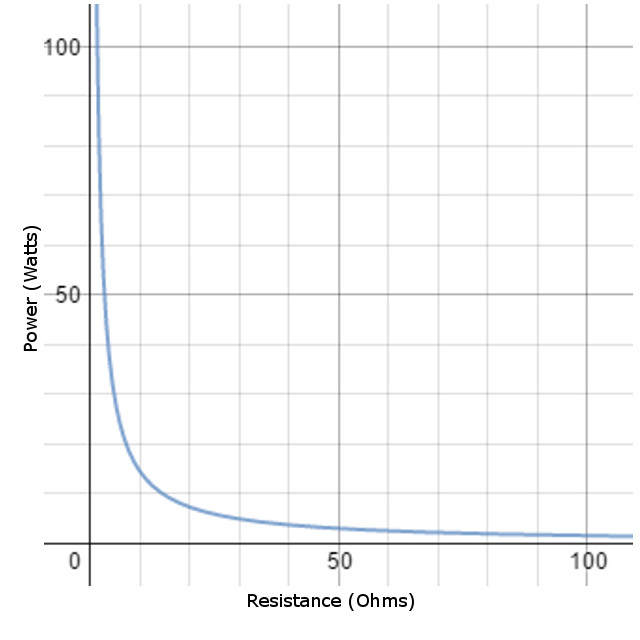
A Graphical Model
Here is a model of how the power dissipated changes as the resistance in a circuit is modified. This graph is based on a constant voltage of 12 volts.
From the graph, it becomes clear that as resistance increases, the power dissipated by the resistor decreases.
Examples
3 varying examples.
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
This topic is extremely important in examining infrastructure related to energy distribution. For example, in power grids, power lines are resistors, and therefore dissipate a certain amount of power. Since resistance is also related to the length of a wire, we can deduce that more power will be dissipated across longer power lines.
Additionally, it is extremely important to understand the concept of power dissipated by a resistor in the field of Electrical Engineering. For example, knowing how to calculate the power dissipated allows for the calculation of how large a resistor needs to be in order handle the energy dissipated through heat.
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page