Speed of Sound in a Solid
This page discusses calculating the speed of sound in various solids and provides examples of such calculations. Claimed by Dpatel322 @ 12/1
The Main Idea
The speed of sound is the speed that sound wave travels through a particular medium. In comparison to air, sound travels considerably faster in solids. The speed that sound travels in various solids depends on the solid's density and elasticity, as these factors effect the ability of the sound waves vibrational energy to transfer across the solid medium.
A Mathematical Model
The speed of sound in solids [math]\displaystyle{ {V_{s}} }[/math] can be determined if the solids elasticity (Young's Modulus value) and density "[math]\displaystyle{ {p} }[/math]" is known.
[math]\displaystyle{ {V_{s}} = √ (Y/p) }[/math]
Youngs Modulus: [math]\displaystyle{ Y ={\frac{Stress}{Strain}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ Stress = {\frac{F_{tension}}{Area_{Cross Sectional}}} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ Strain = {\frac{ΔL_{wire}}{L_{0}}} }[/math]
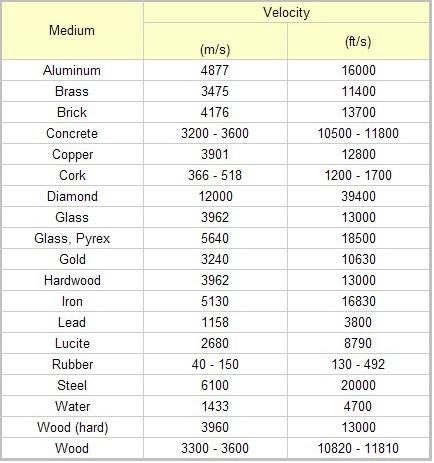
Speeds of Various Compositions
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
The speed of sound in air was first measured by Sir Isaac Newton, and first correctly computed by Pierre-Simon Laplace in 1816. Before this precise measurement, attempts had been made across Europe during the 1700s, most famously Reverend William Derham's experiment in 1709 across the town of Upminister, England. Reverend Derham used a shotgun's noise and several known landmarks around time to measure the time it took for the sound of the blast to be heard from select distances.
Young's Modulus was named after English physicist Thomas Young. In actuality, the concept was developed earlier by physicists Leonhard Euler and Giordano Riccati in the 1720s.
See also
Youngs Modulus: [1] Interatomic Bonds: [2]
Further reading
Further Information can be found on the speed of sound in solids in Matter and Interactions, 4th Edition by Ruth W. Chabay & Bruce A. Sherwood
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page