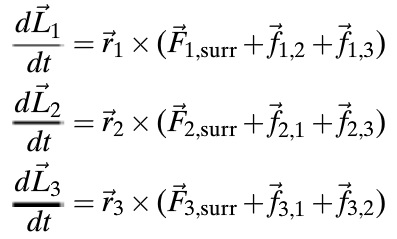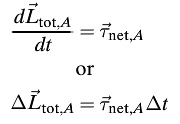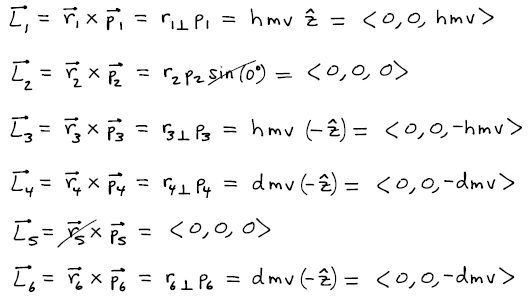Angular Momentum of Multiparticle Systems
The angular momentum principle may be extended to a multiparticle system to provide various insights.
Main Idea
Mathematical Model
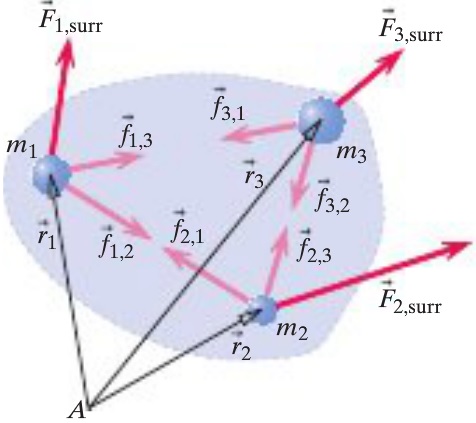
The derivation of the angular momentum principle of a multiparticle system is most easily understood when following a simple example, in this case we will work with a three particle system:
- The angular momentum principle is written for each individual particle relative to location A, with position vectors r and external force vectors F.
- The individual equation is then summed. Note that, due to the reciprocation of forces, the internal forces f cancel out.
- The equation is now rewritten with the right side, representing net torque, as τnet,A
Computational Model
Examples
Simple
Difficult
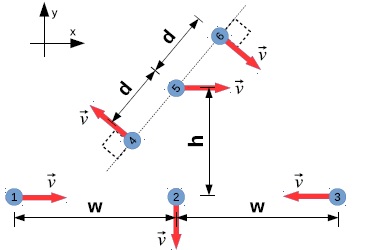
Each of the six particles in the figure have identical mass m and moves in the x-y plane with the same speed v as indicated in the diagram. Take the location of particle 5 as the reference point for all angular momentum calculations when answering the following questions.Be sure to express your answer as a vector.
- What is the momentum of the individual particles?
- Consider the particles above as a single multiparticle system. With respect to particle 5, what is the total angular momentum of the system? What is the translational angular momentum? What is the rotational angular momentum?
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
The Angular Momentum Principle
Multi-particle Analysis of Momentum
External links
The Momentum Principle in Multi-Particle Systems (Video)
Angular momentum of a multi-component system
Chapter 19 Angular Momentum, MIT Course Materials
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page