Light Propagation Through a Medium
This page is going to be about about Light Propagation. A work in progress . Edited by Roshan Konda Fall 2017
The Main Idea
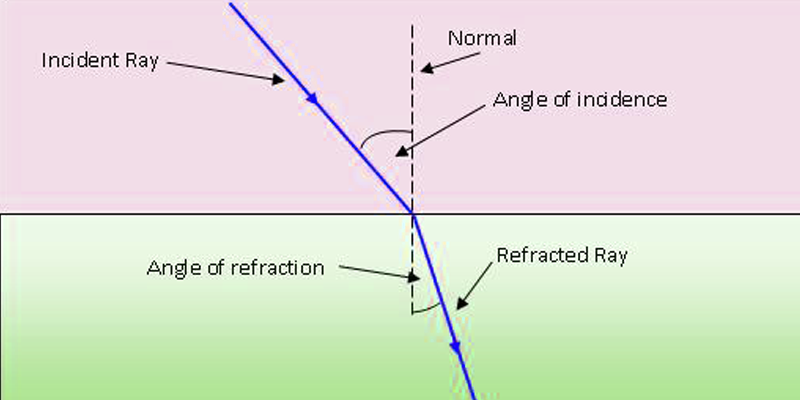
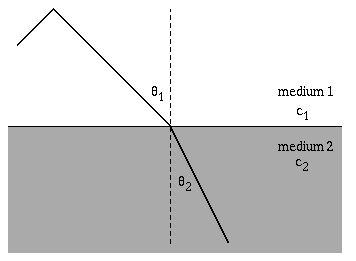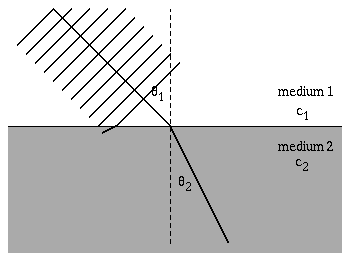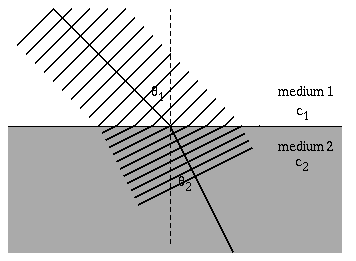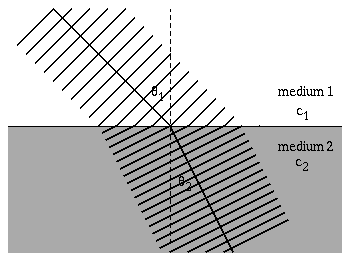
When light travels through anything but a vacuum the speed of light travels at a speed different from c=3.00E8 m/s and the light particles scatter. The highest speed that light can travel though is the universal constant c. Light also refracts, or changes direction when it enters a new medium.
A Mathematical Model
The speed of light through a medium can be given by the formula n=(c/v), where n is the index of refraction, v is the velocity of light through the medium and c is the speed of light through a vacuum. The relationship between the angle of incidence and angle of refraction when light passes through a medium is given by Snell's Law. n1sin(theta1) = n2sin(theta2)
A Computational Model
Examples
Easy
The speed of light is measured to be 2.76E8 m/s, What is the index of refraction for the medium?
Solution
The index of refraction is n=(c/v), n=(3.00E8)/(2.76E8) = 1.09.
Medium
What is the index of refraction of a refractive medium if the angle of incidence in air is 30 degrees and the angle of refraction is 15 degrees?
Solution
solving for n2 in snells law gives (1*sin(30))/sin(15) = 1.93
Difficult
A light ray passes from air into glass at an angle of 20 degrees with respect to the normal. What is the angle of refraction?
Solution
Plugging into Snell's Law gives 1.00sin(20)=1.50sin(theta), solving for theta gives a value of 13.2 degrees.