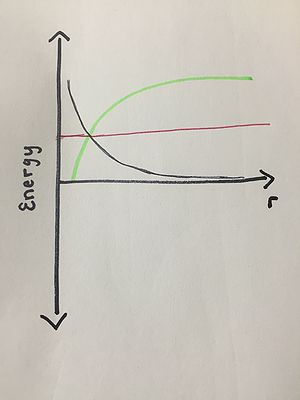
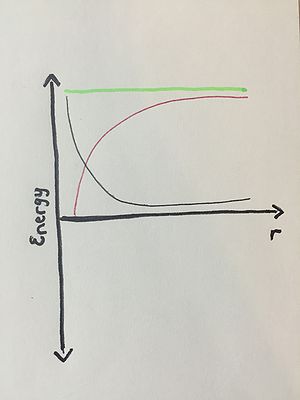
Energy Diagrams
Claimed by Julianne Oliver
The Main Idea
Energy Diagrams are extremely useful for analyzing the interactions between two different objects. These diagrams can also be confusing if not properly understood. This page serves as a resource on how to construct and interpret energy diagrams. Let's get started!
A Mathematical Model
A Computational Model
Vpython is great for modeling this concept. Using vpython, we can model many different systems that have kinetic and potential energy. We can model a spacecraft orbiting the Earth, and we can create graphs to display the kinetic, potential, and kinetic+potential energies of this system. See this code for how to do this!
[Sample Vpython code:https://trinket.io/glowscript/4010e21bc3]
Examples
See end for solutions to all examples.
Simple
Label K, U, and K+U on the energy diagrams for the following situations:
Example 1:
Two electrons are held at rest some finite distance apart, and they move away from each other after they are released. Their initial velocities are zero.
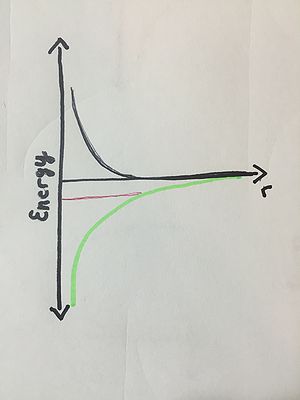
Example 2:
A proton and an electron start out far apart. Their initial velocities are nonzero, and their energy is repulsive.
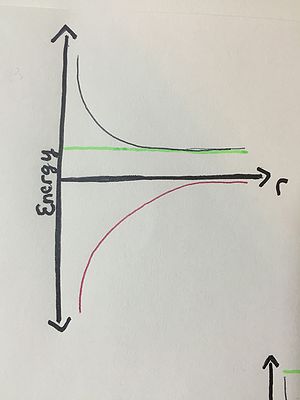
Example 3:
An daughter has just enough energy to escape from her controlling mother (they have an attractive relationship).
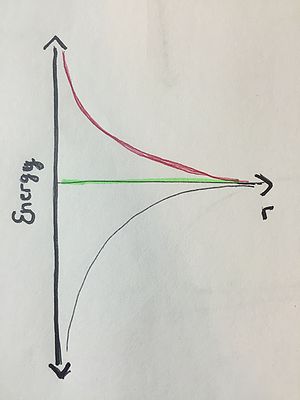
Intermediate
Label K, U, and K+U on the following energy diagrams. THEN, label the following three energy graphs 1, 2, or 3 based on the following scenarios: 1: One of the components of this energy diagram is incorrect. 2: A proton and a electron are at rest, and they start out infinitely far apart. 3: A spacecraft orbits the earth.
Difficult
Create an energy graph for each of the following situations.
Situation 1: A spacecraft is orbiting a moon. The spacecraft is given an initial velocity that allows the spacecraft to leave the moon's orbit with a final velocity greater than zero.
Situation 2: A boy jumps onto a merry-go-round and is attracted to the merry-go-round's axle. The boy's initial velocity is not high enough for him to escape the merry-go-round, so he continues to "orbit" the merry-go-round.
Situation 3: Two people are repulsed by on another and are trying to fight. They are held at rest by two of their friends a finite distant apart, and they of course move away from one another as soon as they are released, since their friends will not let them approach one another.
Solutions to Simple Examples
Example 1: 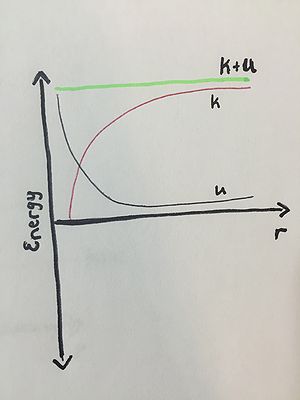
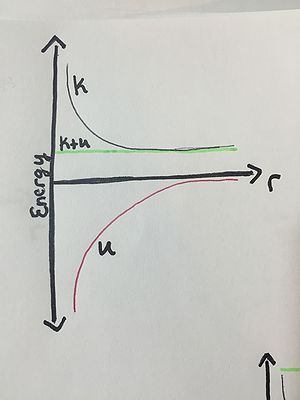
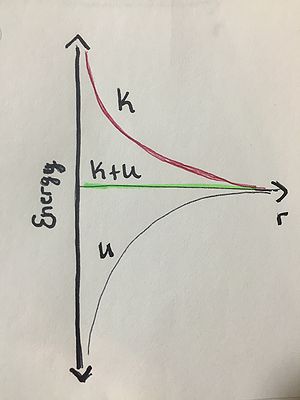
Solutions to Intermediate Examples
Example 1: 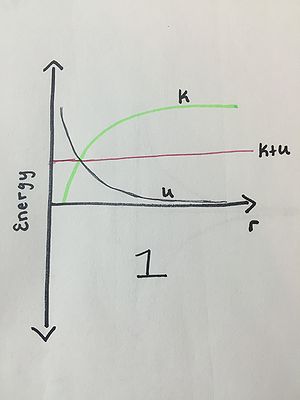
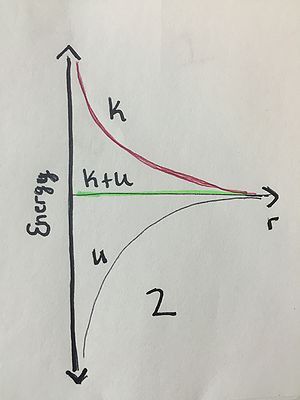
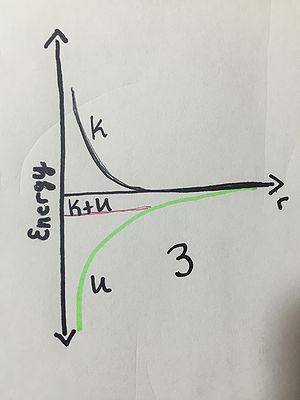
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page