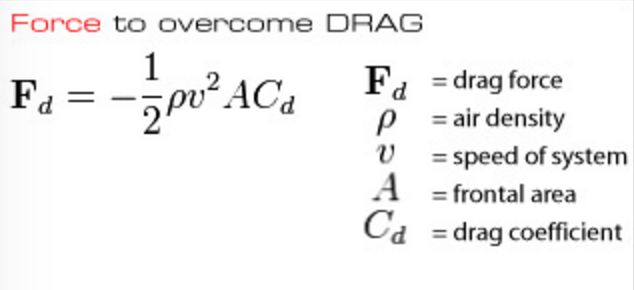Air Resistance
This page is in progress by Jayanth Chintham (jchintham3). 11/29/15
The Main Idea
The forces acting opposite to the direction of motion are called air resistance. Another term for this restraining effect is called "drag." Air resistance is an example of energy dissipation.

You may have noticed that moving objects quickly through any substance is harder than moving objects slowly through a substance. This is due to the air resistance. The magnitude of air resistance directly correlates to the speed of the object. Another feature that impacts air resistance is the cross sectional area of a system. An example is a skydiver with an open parachute has more air resistance than a closed parachute. Air resistance force has an effect on the shape of an object as well. An example of this is a coffee filter, which is blunt object. A ball with the same cross sectional area as a coffee filter has less air resistance.
A Mathematical Model
A Computational Model
[Air Resistance Using Glowscript][1]
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page