Bohr Model
by Pearl Ruparel
Main Idea
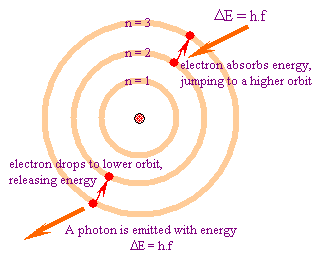
In atomic physics, the Bohr model depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons in orbit similar in structure to the solar system. It is taught as an introduction to quantum physics. In the Bohr Model, electrons can only be at certain, discrete, distances from the proton to which it is bound. If it could be at any distance, it would lose energy (by synchrotron radiation) and eventually spiral into the proton –destroying the atom in the process.
A Mathematical Model
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
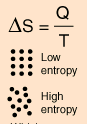
According to philosopher of science Thomas Kuhn, the second law was first put into words by two scientists, Rudolph Clausius and William Thomson (Lord Kelvin), using different examples, in 1850-51. Clausius invented the term in 1865. He had noticed that a certain ratio was constant in reversible, or ideal, heat cycles. The ratio was heat exchanged to absolute temperature. Clausius decided that the conserved ratio must correspond to a real, physical quantity, and he named it "entropy".
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page