Johannes Kepler
Page Claimed by Davis Johnston

Background
What are the mathematical equations that allow us to model this topic. For example [math]\displaystyle{ {\frac{d\vec{p}}{dt}}_{system} = \vec{F}_{net} }[/math] where p is the momentum of the system and F is the net force from the surroundings.
Laws of Planetary Motion
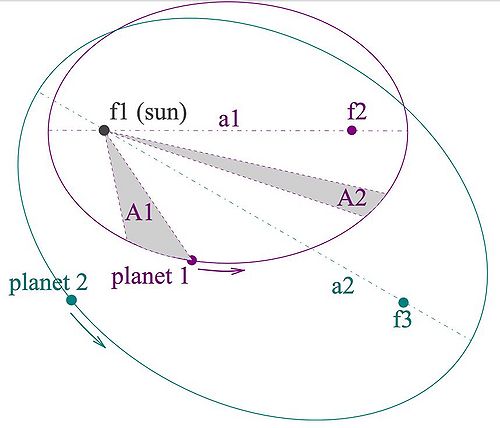
1. Law of Orbits
All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one of the two foci
2. Law of Areas
A line that connects a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
3. Law of Periods
The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi major axis of its orbit.
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page