Compression or Normal Force
Claimed by Hemanth Koralla
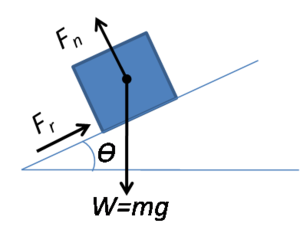
Compression of Normal Force
The compression or also commonly known as the normal force, [math]\displaystyle{ F_n\ }[/math], is a simple fundamental concept that must be understood before attempting any contact force problem. First, it is important to understand that the normal force is NOT a kind of fundamental force such as the electric or gravitational force. It is just a force used to describe the interaction between atoms. As hinted by the name, this force simply points in the perpendicular or "normal" direction to the surface(s) that it is in contact with. The magnitude of this normal force often just the weight of the object, depending on the angle at which object is resting on the other surfaces.
Equation
The formula for calculating the normal force is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_n = mg \cos(\theta) }[/math]
Examples
Time for a few examples:
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/thermo0.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/thereq.html