Semiconductor Devices
claimed by Allison Youngsman 12/2/15
Semiconductor Devices
Semiconductor devices are electronic components with the electronic properties of semiconductors. Silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, organic semiconductors are among the most common semiconductors used in these devices. These "semiconductors" are materials that are neither good conductors or good insulators. Due to low cost, reliability, and compactness, semiconductors are used for a wide range of applications. They also have a wide range of current and voltage handling capabilities, contributing to their suitability for a number of operations. They are commonly found in power devices, optical sensors, and light emitters. Perhaps more importantly, they are readily integrated into microelectronic uses as key elements for the majority of electronic systems, including communications, consumer, data-processing, and industrial-control equipment.
The Main Idea
State, in your own words, the main idea for this topic The two most useful forms of semiconductor devices are diodes and transistors. Diodes are the simplest semiconductor device, which conducts current easily in one direction but conducts almost no current in the other direction. These are made by joining two pieces of semiconducting material,a junction called a "p-n" junction. One of the pieces contains a small amount of boron and the other contains a small amount of phosphorus. Transistors are constructed through two semiconducting junctions, or "p-n" junctions. These are the most common elements in digital circuits. The conductivity of these semiconductors can be controlled by introduction of an electric or magnetic field, by exposure to light or heat, or by mechanical deformation of a doped monocrystalline grid. Due to this, semiconductors are extremely useful and can be altered to fit specific purposes.
A Mathematical Model
Semiconductors operate based on the concept of thermal energy exciting electrons and causing them to jump to the next higher (unoccupied) energy band.
What are the mathematical equations that allow us to model this topic. For example [math]\displaystyle{ {\frac{d\vec{p}}{dt}}_{system} = \vec{F}_{net} }[/math] where p is the momentum of the system and F is the net force from the surroundings. These electrons can pick up energy (and drift speed) from an applied electric field. The filled energy band is called the “valence” band, and the nearly unoccupied higher energy band is called the “conduction” band. The number of electrons excited into the conduction band is proportional to a value called the Boltzmann constant, equivalent to the value:

Therefore, high conductivity (corrosponding to a favorable Boltzmann factor) can be calculated according to

In addition, the total conventional current in a semiconductor can be calculated, according to the equation 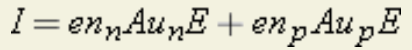
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Moderate
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
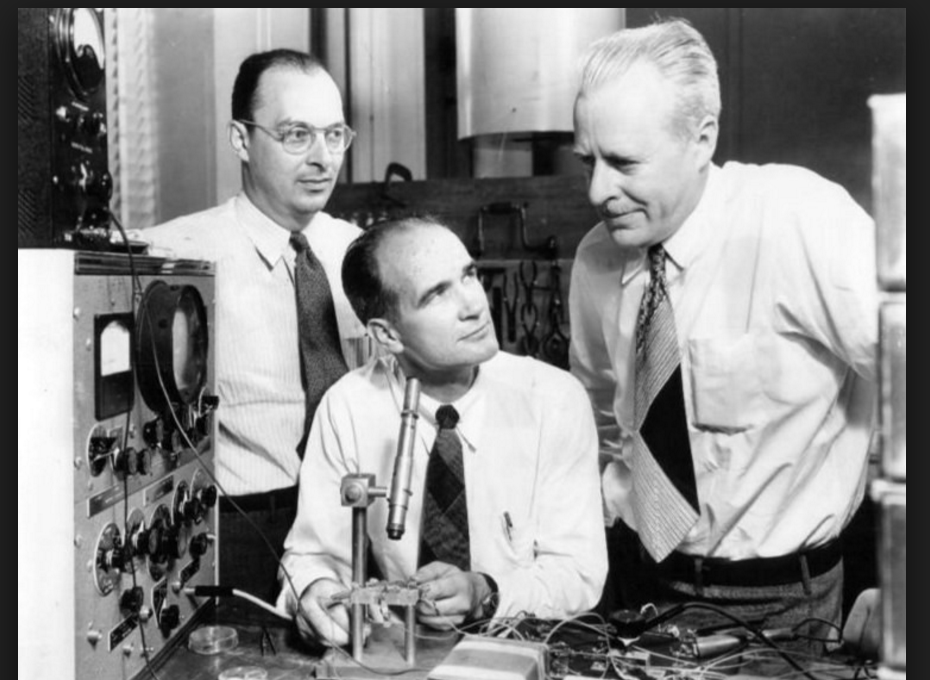
The studying of semiconductor materials first began around the beginning of the 19th century. Prior to 1947, semiconductors were used only as two-terminal devices, such as rectifiers and photodiodes. They were most commonly used as detectors in radios, through devices called "cat's whiskers". During the era of WWII, researchers worked with semiconductors and cat's whiskers to make more effective diodes. After the war, two researchers named William Shockley and John Bardeen worked together to create a triode-like semiconductor: the first transistor. They realized that if there were some way to control the flow of the electrons from the emitter to the collector of this newly discovered diode, an amplifier could be built.The first transistor was officially created on the 23rd of December, 1947. John Bardeen, William Shockley, and another researcher named Walter Houser Brattain were credited for the invention and awarded a Nobel Prize for physics in 1956 for their work. After this, the utilization of semiconductors soon advanced to even more complicated applications. In the late 1960s, transistors moved from being germanium based to silicon based. Gordon K Teal was most responsible for this advancement, and his company, Texas Instruments, profited greatly. Portable radios are just one popular invention that benefited from silicon based semiconductors. Now, silicon based semiconductors constitute more than 95 percent of all semiconductor hardware sold worldwide.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page