Heinrich Hertz
The renowned scientist Heinrich Hertz was the first physicist to prove the existence of electromagnetic waves which was hypothesized in James Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism.

Personal Life
German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born on February 22, 1857 into a prosperous and cultured Hanseatic (hierarchy group that constituted the ruling class of Hamburg) family. His father, Gustav Hertz, was a lawyer and later a senator, his mother, Anna Elisabeth Pfefferkorn, was the daughter of a physician, and Heinrich Hertz was the oldest of five children. Both parents were Lutherans but they were more interested in Hertz's education rather than his religious advancement. From the beginning of his education, Hertz was always at the top of his class. He had an uncommon gift for modern and ancient languages; he excelled in Greek at school while taking private lessons in Arabic at the same time. Hertz also had extraordinary aptitudes for mathematics and the sciences. Hertz was homeschooled for a little while before deciding to return to school to prepare him for exams that would admit him to a university. After being an architect's apprentice, completing his army service, and choosing to major in engineering, Hertz finally decided that he wanted to become a physicist. He enrolled in the University of Munich before moving to the University of Berlin to pursue his higher education in physics under Hermann von Helmholtz. In 1880, Hertz received a Ph.D. magna cum laude from the University of Berlin. He then went on to become a professor at the University of Karlsruhe in 1885 and married Elisabeth Doll, the daughter of a lecturer in geometry at Karlsruhe. They had two daughters, Johanna (1887) and Mathilde (1891), who later became a notable biologist. It was during this time that Hertz conducted his prominent research into electromagnetic waves. He also worked on theoretical mechanics and wrote a book. In 1892, Hertz suffered the first signs of serious health problems. He died of granulomatosis with polyangiitis on January 1, 1894 at the age of 36. His book on theoretical mechanics Die Prinzipien der Mechanik was published after his death.
Discovery of Radio Waves
James Maxwell's Theory
In 1865, Scottish scientist James Maxwell came up with the theory of electromagnetism, which is one of the main pillars of modern theoretical physics. In his theory, Maxwell predicted that electromagnetic waves do exist. By constructing an oscillating electrical circuit, he showed that electromagnetic waves could move through empty space. He proposed that light (and other forms of radiant energy) is an electromagnetic disturbance in the form of waves.
The Beginning
While Hertz was at Karlsruhe, he decided that the focus of his research should be on proving Maxwell's theory of electromagnetic radiation. One day, Hertz was showing his students electric sparks. He performed a series of experiments that generated sparks in various ways. Through these experiments, Hertz discovered that the sparks were producing a regular electrical vibration within the electric wires they jumped between. According to Hertz, the vibration moving back and forth was more often every second than what he had ever encountered before. He knew that the vibration was made up of rapidly accelerating and decelerating electric charges. Hertz began to wonder that if Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism was correct, the electric charges would radiate electromagnetic waves which would pass through the air as light.
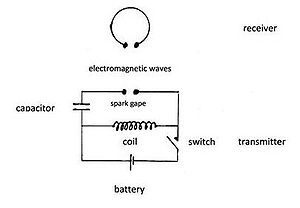
The Oscillator

In 1886, Hertz created the oscillator, his first radio transmitter, which was an apparatus consisting of a pair of one meter copper wires with 30 cm zinc spheres at the end. He used a coil-driven spark gap and the wire as a radiator and his receiver was a half-wave dipole antenna. He applied high-voltage across the central spark-gap, which created sparks and the sparks in turn caused violent pulses of electric current within the copper wires. These pulses vibrated within the wires and just as James Maxwell had predicted in his electromagnetic theory, the oscillating electric charges produced electromagnetic waves. These waves were radio waves and they spread out through the air around the wires. Hertz had produced and detected radio waves. He passed electrical energy through the air from device to another with no use of connecting wires.
Further Research
Hertz performed more experiments and was soon able to fully verify Maxwell's theory. He demonstrated that the energy radiating from his electrical oscillators could be reflected, refracted, and could produce interference patters and standing waves similar to light. His experiments, in fact, provided evidence that radio waves and light waves came from what we call today the electromagnetic spectrum.

Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
See also
Further reading
Bryant, John H., Heinrich Hertz, the beginning of microwaves: discovery of electromagnetic waves and opening of the electromagnetic spectrum by Heinrich Hertz in the years 1886-1892, New York: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers; Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Service Center, Single Publication Sales Dept. distributor, 1988.
Buchwald, Jed Z. 1994. The Creation of Scientific Effects: Heinrich Hertz and Electric Waves. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Heinrich Hertz, The Principles of Mechanics Presented in a New Form. Dover Phoenix Editions.
Heinrich Hertz, Electric waves: Being researches on the propagation of electric action with finite velocity through space.
Lützen, Jesper. 2005. Mechanistic Images In Geometric Form: Heinrich Hertz's Principles of Mechanics. New York: Oxford University Press.
External links
http://earlyradiohistory.us/1901hz.htm
References
http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Heinrich_Rudolf_Hertz.aspx
http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Heinrich_Hertz