Loop Rule
The Loop Rule is a fundamental principle of electric circuits that claims that in any round trip path in a circuit, Electric Potential equals zero.
Loop Rule
The loop rule simply states that in any round trip path in a circuit, Electric Potential equals zero. This principle deals with the conservation of energy within a circuit. Loop Rule and Node Rule are the two fundamental principle of electric circuits and are used to determine the behaviors of electric circuits.
A Mathematical Model
A mathematical representation is: [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta {V}_{1} + \Delta {V}_{2} + \space.... = 0 }[/math]
This can also be represented in a circuit as [math]\displaystyle{ emf = \Delta {V}_{1} + \Delta {V}_{2} + \space..... }[/math]
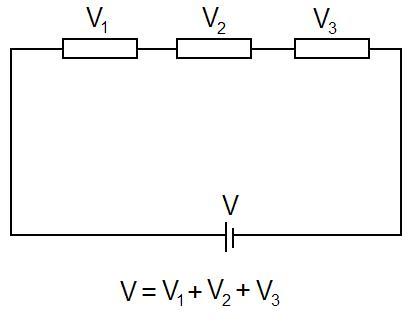
A Visual Model
The total voltage in the circuit is equal to all the individual voltages in the circuit added together.
Another way to think about it is [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta {V} - (\Delta {V}_{1} + \Delta {V}_{2} + \Delta {V}_{3})= 0 }[/math]
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
History
The Loop Rule is formally known as the Kirchhoff Circuit Law, named after Gustav Kirchhoff discovered and defined this fundamental concept of electric circuits.
He discovered this during his time as a student at Albertus University of Königsberg in 1845.
Kirchoff went on to explore the topics
of spectroscopy and black body radiation after his graduation from Albertus. /tab 
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
See also
Other Circuit Concepts
More Information and External links
Kirchoff's Circuit Laws - Wikipedia
Loop Rule - Boundless.com Textbook
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page
Claimed by Bmock7