Detecting a Magnetic Field: Difference between revisions
Ejohnston8 (talk | contribs) |
Ejohnston8 (talk | contribs) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==The Main Idea== | ==The Main Idea== | ||
[[File:Magnetic Field around a wire.png|200px|thumb|right|This shows the Magnetic Field around a wire. The field above and below are in opposite directions which Oerested determined.]] | |||
A compass can be used to determine the magnetic field in a wire. If a compass is not in the proximity of any iron or steel object, the compass will naturally point in the direction of the Earth's magnetic north pole. If a current carrying wire is brought near the compass, the compass needle will deflect in the direction of the net magnetic field. | A compass can be used to determine the magnetic field in a wire. If a compass is not in the proximity of any iron or steel object, the compass will naturally point in the direction of the Earth's magnetic north pole. If a current carrying wire is brought near the compass, the compass needle will deflect in the direction of the net magnetic field. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Net Field.png|200px|thumb|left|Net Magnetic Field]] | ||
===A Mathematical Model=== | ===A Mathematical Model=== | ||
A useful attribute of a compass is that you can calculate the the magnetic field of current carrying wire when you figure out the deflection angle. This equation is: <math>B_{wire}=B_{earth} tan(\theta)</math> where <math>\theta</math> is the deflection angle, <math>B_{earth}</math> is the earth's magnetic field which is a constant value of 2e-5 Tesla. | A useful attribute of a compass is that you can calculate the the magnetic field of current carrying wire when you figure out the deflection angle. This equation is: <math>B_{wire}=B_{earth} tan(\theta)</math> where <math>\theta</math> is the deflection angle, <math>B_{earth}</math> is the earth's magnetic field which is a constant value of 2e-5 Tesla. | ||
===A Computational Model=== | ===A Computational Model=== | ||
Take a minute to watch this video | Take a minute to watch this video showing Oersted's Experiment. It is very similar to what we did in lab. | ||
[https://www.youtube.com/embed/lwjk789NaVQ?rel=0 Video Showing Oersted Effect] | [https://www.youtube.com/embed/lwjk789NaVQ?rel=0 Video Showing Oersted Effect] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 43: | ||
When you bring a current-carrying wire down onto the top of a compass, aligned with the original direction of the needle and 4 mm above the needle, the needle deflects by θ = 12 degrees (see the figure). | When you bring a current-carrying wire down onto the top of a compass, aligned with the original direction of the needle and 4 mm above the needle, the needle deflects by θ = 12 degrees (see the figure). | ||
[[File:Problem 17.7.035 from Matter and Interactions Book.png|200px|thumb| | [[File:Problem 17.7.035 from Matter and Interactions Book.png|200px|thumb|center| | ||
*The magnetic field under the wire, due to the current, points East. | *The magnetic field under the wire, due to the current, points East. | ||
*Electron current in the wire is flowing upward(North). | *Electron current in the wire is flowing upward(North). | ||
| Line 46: | Line 50: | ||
Calculate the amount of conventional current flowing in the wire. The measurement was made at a location where the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is <math>B_{Earth}= 2 ✕ 10^{-5}</math> tesla. | |||
<math>B_{wire}=B_{earth} ✕ tan(\theta)</math> | <math>B_{wire}=B_{earth} ✕ tan(\theta)</math> | ||
| Line 109: | Line 98: | ||
Given: | Given: | ||
<math> B_{wire}=5.735e-6 | <math>B_{wire}</math>=5.735e-6 T, r= 0.003 m, and <math>{\mu_{0}\over4\pi}=1e-7;</math> Solve for the current :I | ||
<math>{5.735e-6}={1e-7}{2I\over .003}</math> | <math>{5.735e-6}={1e-7}{2I\over .003}</math> | ||
| Line 125: | Line 114: | ||
==Connectedness== | ==Connectedness== | ||
There are many applications of the idea behind this topic. There are many electromagnetic devices where you are able to manipulate the magnetic field by varying the current running through the device. | There are many applications of the idea behind this topic. There are many electromagnetic devices where you are able to manipulate the magnetic field by varying the current running through the device. | ||
A good example is a speaker. There are electromagnets inside of the speaker and when you vary the current running through the wires around them you vary the output of the speaker. | A good example is a speaker. There are electromagnets inside of the speaker, and when you vary the current running through the wires around them, you vary the output of the speaker. | ||
Any engineering major knows that there is a great amount of physics behind what you do. Physics and engineering are heavily intertwined. | Any engineering major knows that there is a great amount of physics behind what you do. Physics and engineering are heavily intertwined. | ||
| Line 134: | Line 123: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
There are many other wiki pages relating to magnetic fields in this physics wiki. One I would recommend is | There are many other wiki pages relating to magnetic fields in this physics wiki. One I would recommend is: | ||
:[[Biot-Savart Law for Currents|Biot-Savart Law for Currents]] | :[[Biot-Savart Law for Currents|Biot-Savart Law for Currents]] | ||
This page gives the equation used to find the magnetic field when given a current which is what we used in this page. The math can explain the concept of the current changing the magnitude of the magnetic field. This magnetic field causes the deflection of the compass. | This page gives the equation used to find the magnetic field when given a current which is what we used in this page. The math can explain the concept of the current changing the magnitude of the magnetic field. This magnetic field causes the deflection of the compass. | ||
===Further reading=== | ===Further reading=== | ||
[https://www.physics.ncsu.edu/physics_ed/Articles/LunkBFieldArticle.pdf| Exploring Magnetic Fields With a Compass] | |||
Article describing what happens when a compass is brought near a current carrying wire. | |||
===External links=== | ===External links=== | ||
[http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/magfie.html| Magnetic Fields] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 153: | Line 144: | ||
32 Oersted's Effect.mpg. Perf. Science Demo LTD. Youtube. N.p., 24 Oct. 2010. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwjk789NaVQ>. | 32 Oersted's Effect.mpg. Perf. Science Demo LTD. Youtube. N.p., 24 Oct. 2010. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwjk789NaVQ>. | ||
Page initiated by --[[User:Ejohnston8|Ejohnston8]] | Lunk, Brandon, and Robert Beichner. "Exploring Magnetic Fields With a Compass." The Physics Teacher 49 (2011): 45-48. 2011. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <https://www.physics.ncsu.edu/physics_ed/Articles/LunkBFieldArticle.pdf>. | ||
Magnetic Field." Hyperphysics. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/magfie.html>. | |||
Page initiated by --[[User:Ejohnston8|Ejohnston8]] | |||
[[Category:Fields]] | [[Category:Fields]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:03, 29 November 2015
The Main Idea
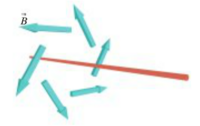
A compass can be used to determine the magnetic field in a wire. If a compass is not in the proximity of any iron or steel object, the compass will naturally point in the direction of the Earth's magnetic north pole. If a current carrying wire is brought near the compass, the compass needle will deflect in the direction of the net magnetic field.

A Mathematical Model
A useful attribute of a compass is that you can calculate the the magnetic field of current carrying wire when you figure out the deflection angle. This equation is: [math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}=B_{earth} tan(\theta) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \theta }[/math] is the deflection angle, [math]\displaystyle{ B_{earth} }[/math] is the earth's magnetic field which is a constant value of 2e-5 Tesla.
A Computational Model
Take a minute to watch this video showing Oersted's Experiment. It is very similar to what we did in lab. Video Showing Oersted Effect
Examples
Simple
Problem 17.2.XP.003 from Matter and Interactions Book:
A current-carrying wire oriented north-south and laid over a compass deflects the compass 18° to the east. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field made by the current? The horizontal component of Earth's magnetic field is about [math]\displaystyle{ 2 ✕ 10^{-5} tesla }[/math] .
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}=B_{earth} tan(\theta) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}= 2 ✕ 10^{-5} tesla ✕ tan(18) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}= 6.49✕ 10^{-6} }[/math]Tesla
What direction does the electron current flow in the wire?
The electron current flows from south to north.
Middling
Problem 17.7.035 from Matter and Interactions Book:
Deflecting a compass needle
When you bring a current-carrying wire down onto the top of a compass, aligned with the original direction of the needle and 4 mm above the needle, the needle deflects by θ = 12 degrees (see the figure).

Calculate the amount of conventional current flowing in the wire. The measurement was made at a location where the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is [math]\displaystyle{ B_{Earth}= 2 ✕ 10^{-5} }[/math] tesla.
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}=B_{earth} ✕ tan(\theta) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}= 2 ✕ 10^{-5} tesla ✕ tan(12) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}= 4.25✕ 10^{-6} }[/math]Tesla
Given: [math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}= 4.25✕ 10^{-6} }[/math]Tesla, r=.004 m,[math]\displaystyle{ {\mu_{0}\over4\pi}=1e-7 }[/math]; Solve for I:
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}={\mu_{0}\over4\pi}{2I\over r} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ 4.25✕ 10^{-6}=1e-7{2I\over .004} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ I={{.004✕4.25✕ 10^{-6}}\over {2✕ {1✕ 10^{-7}}}} }[/math]
I=.085 Amperes
Difficult
Problem 17.7.038 from Matter and Interactions Book:
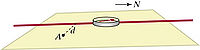
A long current-carrying wire, oriented North-South, lies on a table (it is connected to batteries which are not shown). A compass lies on top of the wire, with the compass needle about 3 mm above the wire. With the current running, the compass deflects 16 degrees to the West. At this location, the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is about 2e-5 tesla.
What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at location A, on the table top, a distance 2.5 cm to the East of the wire, due only to the current in the wire?
Solving:
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}=B_{earth}tan(\theta) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}=2e-5*tan(16) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}=5.735e-6 T }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}={\mu_{0}\over4\pi}{2I\over r} }[/math] Where r is the distance the wire is from the compass.
Given: [math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire} }[/math]=5.735e-6 T, r= 0.003 m, and [math]\displaystyle{ {\mu_{0}\over4\pi}=1e-7; }[/math] Solve for the current :I
[math]\displaystyle{ {5.735e-6}={1e-7}{2I\over .003} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {{{5.735e-6}*{.003}}\over{1e-7 *2}}={I} }[/math]
I=.086 A
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}={\mu_{0}\over4\pi}{2I\over d} }[/math] Now solve for the new [math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire} }[/math] given the current: I=.086 A and the new location d= .025m
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}={1e-7} {{2*.086}\over .025} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ B_{wire}= }[/math]6.882 e-7 T
Connectedness
There are many applications of the idea behind this topic. There are many electromagnetic devices where you are able to manipulate the magnetic field by varying the current running through the device. A good example is a speaker. There are electromagnets inside of the speaker, and when you vary the current running through the wires around them, you vary the output of the speaker.
Any engineering major knows that there is a great amount of physics behind what you do. Physics and engineering are heavily intertwined.
History

This phenomenon was discovered by Danish scientist, Hans Oersted in 1826. After stumbling upon the deflection of a needle, he further investigated the math behind the event. He discovered that the magnitude of the magnetic field depends on the amount of current; if there is no current there will be no magnetic field. He also discovered that the deflection direction of the compass when the wire is above the wire is opposite the deflection direction when the wire is below the wire. This was the start of understanding magnetic fields.
See also
There are many other wiki pages relating to magnetic fields in this physics wiki. One I would recommend is:
This page gives the equation used to find the magnetic field when given a current which is what we used in this page. The math can explain the concept of the current changing the magnitude of the magnetic field. This magnetic field causes the deflection of the compass.
Further reading
Exploring Magnetic Fields With a Compass Article describing what happens when a compass is brought near a current carrying wire.
External links
References
Chabay, R. & Sherwood, B. (2015). Matter and Interactions(4th Ed)(Vol 2). North Carolina: John Wiley & Sons,Inc.
Hans Christian Oersted. Digital image. MagCraft. National Imports, 2015. Web. 18 Nov. 2015. <http://www.rare-earth-magnets.com/hans-christian-oersted/>
Kurtus, Ron. "Electromagnetic Devices." By Ron Kurtus. School for Champions. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/electromagnetic_devices.htm#.Vlsxtd-rTVo>..
32 Oersted's Effect.mpg. Perf. Science Demo LTD. Youtube. N.p., 24 Oct. 2010. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwjk789NaVQ>.
Lunk, Brandon, and Robert Beichner. "Exploring Magnetic Fields With a Compass." The Physics Teacher 49 (2011): 45-48. 2011. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <https://www.physics.ncsu.edu/physics_ed/Articles/LunkBFieldArticle.pdf>.
Magnetic Field." Hyperphysics. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2015. <http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/magfie.html>.
Page initiated by --Ejohnston8