Magnetic Dipole: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
If released from rest, what, if anything, will the current loop do? | If released from rest, what, if anything, will the current loop do? | ||
[[File: | [[File:Current_loop_magfield.JPG]] | ||
'''Solution''' | '''Solution''' | ||
Revision as of 00:26, 7 April 2017
Claimed by Priya Patel (Spring 2017)
The Main Idea
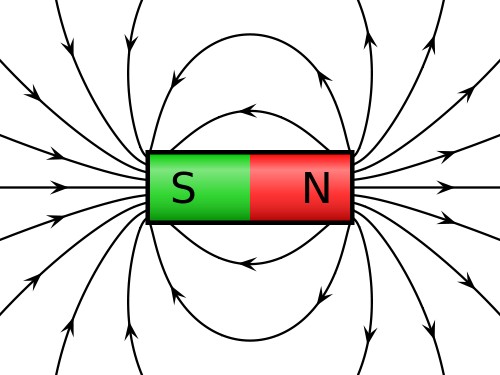
A magnet will produce a magnetic field everywhere in space. This is very similar to electrostatics, but instead of charges, we have North and South poles. Like poles repel, and unlike poles attract. Since magnets always come in North/South pairs (link to history section about monopoles), the magnetic field produced is that of a magnetic dipole, which looks very similar to the electric dipole field. The North pole is analogous to a positive charge and South to a negative charge, in that the field lines flow out from the North pole into the South pole.
A Mathematical Model
The equation for a magnetic dipole moment is:
[math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol{\mu} = \boldsymbol{IA} = \boldsymbol{I{\pi}R^2} }[/math] with units [math]\displaystyle{ A*m^2 }[/math]
where I is the current, and A is the cross sectional area. This will be used to calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field produced by a magnetic dipole.
The 2nd part of the equation is specifically for a circular loop field induced magnetic dipole and its area is the area of the loop.
From this equation, we can deduce the magnetic dipole moments just knowing the conventional current flowing through the loop and the radius.
However, most of the time the current is not given. Furthermore, the equation is not applicable for the normal bar magnets, for they do not have a electrical current flowing through. Thus, another way to get the dipole moment is by using the relationship between the magnetic dipole and the magnetic field induced by the dipole.
There are two equations based on the observation location.
Observation Location Perpendicular to Dipole Axis
If the observation location is perpendicular to the axis of the dipole(see below),
then the equation for the magnetic field induced by the dipole is:
Note that this equation is analogous to the equation for an observation location perpendicular to the axis of an electric dipole.
Observation Location Along Dipole Axis
If the observation location is placed along the axis like in the image below,
then the equation for the magnetic field induced by the dipole is:
Note that this equation is analogous to the equation for an observation location perpendicular to the axis of an electric dipole.
The first part of the equation is the constant, 1E-7, and the other part of the equation requires the magnetic dipole and the distance between the observation location and the dipole denoted by r.
Direction of Dipole Moment
It is also important to note the direction of the dipole moment. The direction of the dipole moment points North in a magnet:
On the other hand, if you are looking at the dipole moment induced by a current-flowing loop, you have to use the right hand rule. Curl your fingers in the direction of the current, and your thumb will point in the direction of the magnetic dipole moment induced from the current.
Examples
Simple
In a circular loop with current of 3 Ampere and diameter of 16 cm, what is the magnetic dipole moment induced from the current?
Solution
We can just simply use the first equation given in the beginning:
where R is 0.08 meters and I is 3 Amperes. Calculating for the magnetic dipole moment gives:
[math]\displaystyle{ 3 \times 0.08^2 \times \pi = 0.0192 A*M^2 }[/math]
Middling
When a compass is placed 20 cm away from a bar magnet parallel to the x-axis and shows deflection of 20 degrees, what is the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment? You can assume that |Bearth| is [math]\displaystyle{ 2 \times 10^-5 T }[/math]
Solution
First, we need to figure out the magnetic dipole induced from the magnet. Thus, we need to use the formula:
where |Bearth| is [math]\displaystyle{ 2 \times 10^-5 T }[/math], and the deflection is 20 degrees. Thus,
[math]\displaystyle{ (2E-5 T) * tan(20) = 7.3E-6 T }[/math]
This gives us the magnitude of the magnetic field contributed by the bar magnet. We can plug in the value into the formula given (note that because it is along the x-axis, we use this formula)
[math]\displaystyle{ 7.3E-6 = \frac {1E-7 * 2 * \mu} {(0.2)^3} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \mu = 0.292 A*M^2 }[/math]
Conceptual Question
If released from rest, what, if anything, will the current loop do?
Solution
The loop will rotate counterclockwise. We know this because the magnetic dipole moment has a tendency to want to align itself with any externally applied magnetic field, if one exists. Using the right-hand rule for a loop of current, we curl our fingers clockwise, causing our thumb to point straight downwards. This means that our magnetic dipole moment is poiting straight downwards. In order to align itself with the magnetic field that is pointing to the right, it must rotate counterclockwise.
Connectedness
Industrial Application
One of the most common industrial applications of Magnetic Dipole is the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy. To learn more about NMR, click here
History
Magnetic Monopoles
Although electrostatics and magnetics have a lot in common, one difference is that magnetic poles cannot exist singly like charges can. Poles always come in N/S pairs. If you were to cut a bar magnet in half, you will get two new magnets with North and South poles.
A magnetic monopole was observed once, by Blas Cabrera, on February 14, 1982 (also known as the Valentine's Day Monopole). However, this experiment has been recreated several times, and no one, not even Cabrera himself, has been able to find another monopole.
See also
Magnetic Field of a Long Straight Wire
Further reading
Terahertz Magnetic Response from Artificial Materials
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/303/5663/1494